As indicated by this Forbes article, 76% of customers contact businesses to make inquiries and get support via text messaging. Now with the required social distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic, more and more consumers choose to interact with brands online.
Many businesses now receive hundreds or even thousands of customer inquiries daily. Let's assume that each customer service agent could handle about 30 calls per day, doubling the estimate in this report, it would need 10 human agents to answer about 300 incoming customer inquiries. On the other hand, short of manpower implies the prolonged customer waiting time and a Forrester study shows that 2 out of 3 customers don't want to wait for more than 2 minutes to get assistance.
To cope with the increasing volume of customer interactions, businesses started to look for solutions to automate customer interactions. One promising solution is to use a chatbot to augment human agents and help answer repetitive questions, such as "How to reset my password", "What is your refund policy" and "Where can I download your mobile apps". Even better, a chatbot can be trained to handle complex questions that require multi-turn interactions, such as "Can you find an online tutor for me?" and "Could you show me how to use your product?"
Challenges for Making Customer Service Chatbot
However, setting up a capable chatbot for customer services may be non-trivial, since a customer service chatbot must have a set of key capabilities to deliver satisfactory customer experiences. From our own experiences of helping organizations set up and manage customer service chatbots, we have discovered that a customer service chatbot often fails to fulfill its purpose because one of the following reasons.
Lack of Natural Language Processing (NLP)
If a chatbot does not have any Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities, it won't understand a user's natural language inquiries. A chatbot without AI or NLP is most likely to force users to traverse a tree-based menu by clicking on the displayed choices one by one before finding or not finding the answers they want. This approach never works well even if your business is super simple for two reasons. First, such a tree-based menu is often limited with choices and can hardly include every answer to customer questions. Second, customers may not know which path to take or which option to select.
For example, on an e-learning website, I want to find out which SEO course would be suitable for a beginner like me. It would be hard to insert such an answer in a tree-based menu. In another example, if I want to know whether I can get a free trial of a particular product, should I traverse the path to "Product" or "Price"?
It is worth mentioning an often used "NLP" technique supported by some chatbot platforms is keyword spotting, which retrieves potential answers based on certain keywords mentioned in a user's question. Unfortunately, keyword-based processing is often inadequate for a customer service chatbot because it cannot distinguish the semantic differences between customer questions containing the same keywords. Consider these two questions both containing the keyword "refund":
"Can I get a refund for the course I paid for"
"When will I receive my refund"
Users would not be happy if they ask the latter question but get the answer to the former question, or vice versa.
Here is a short Youtube video showing the difference between understanding the keywords vs. the semantics of user input.
Lack of Abilities to Handle Interruptions
As a customer, you may have experienced such a frustration with an incapable chatbot: you asked for a service, e.g., getting an insurance quote, and you had followed the chatbot instructions down for 5 steps already. But you had a question near the last step so you asked the question. Poof, all you had done so far was lost and you had to start over again. That is because such a chatbot does not know how to handle out-of-flow interruptions or has no concept of context. Once it is interrupted, the chatbot could not resume its original flow but restarts. As you can imagine, how frustrated a customer could be when encountering such a situation! Again, the same Forrester study shows that 63% customers abandon a company after just one bad experience.
Lack of Abilities to Help Human Agents
No chatbot is perfect and it cannot answer every customer question. It thus is very important for a chatbot platform to have the abilities to monitor a chatbot activities in real time, know when a chatbot fails, and notify human agents of chatbot failures so they can help address the gap.
Ideally, a chatbot platform should also help a human agent better handle the handed-over, unresolved issues, such as suggesting potential answers or knowing the emotional state of the users involved. Many chatbot platforms support chatbot-human handoff, but few can truly aid human agents in resolving the issues efficiently let alone understanding the users involved.
Difficult to Setup and Update AI Chatbots
Some chatbot platforms may support all the three capabilities mentioned above. However, it may take a team of engineers months to set up a customer service chatbot and weeks to update such a chatbot, e.g., updating the chatbot's knowledge base to improve its performance. Moreover, most platforms require AI expertise (e.g., defining intents and entities) or programming experience (e.g., manually wiring all different intents and re-prompting) to power a customer service chatbot with AI capabilities described above. With such a long turnaround time and difficulties in the chatbot upkeep, organizations may hesitate taking the steps to consider let alone implement a customer service chatbot.
Three Steps to Power Customer Service Chatbots with AI
To address the challenges in the adoption and upkeep of customer service chatbots as discussed above, Juji platform is designed to enable organizations to build and manage effective customer service chatbots rapidly. Specifically, the Juji Studio radically simplifies the teaching of AI and enables non-IT professionals to build and manage powerful AI chatbots for customer services in three steps, and no coding required.
Step 1. Prepare a free-text Q&A list
The main function of a customer service chatbot is to answer customer inquiries. As mentioned above, customer inquiries may be highly diverse, in both natural language expressions and topics. A tree-based menu can hardly satisfy customer needs. To deliver exceptional customer experience, a customer service chatbot should be able to understand customer free-text inquiries and respond accordingly.
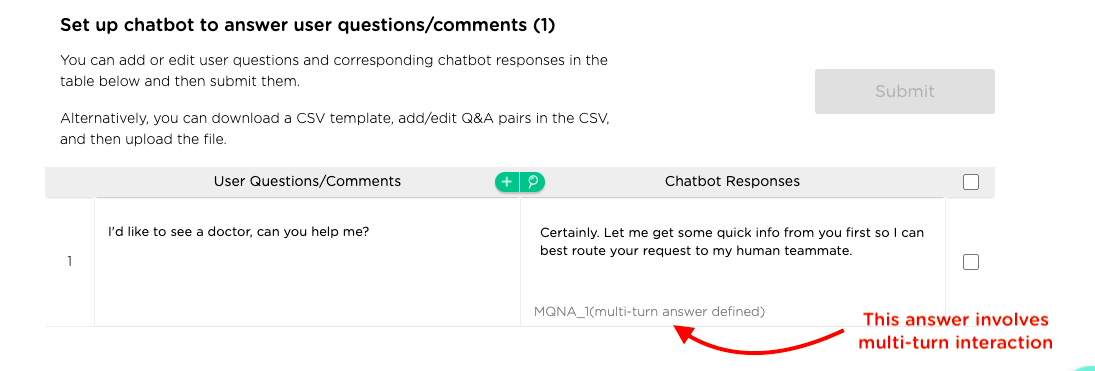
To power a chatbot with free-text Q&A capabilities, Juji enables you to easily teach a chatbot in one of two ways. First, you can enter Q&A pairs directly in a table as shown below:
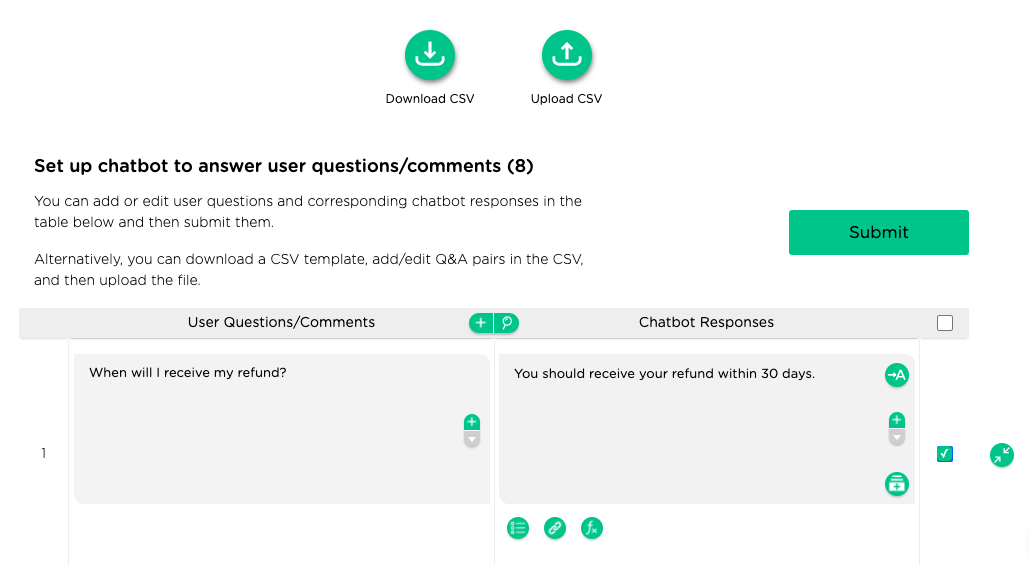
Once the entered Q&A pairs are submitted (using the "Submit" button), a chatbot is enabled for free Q&A.
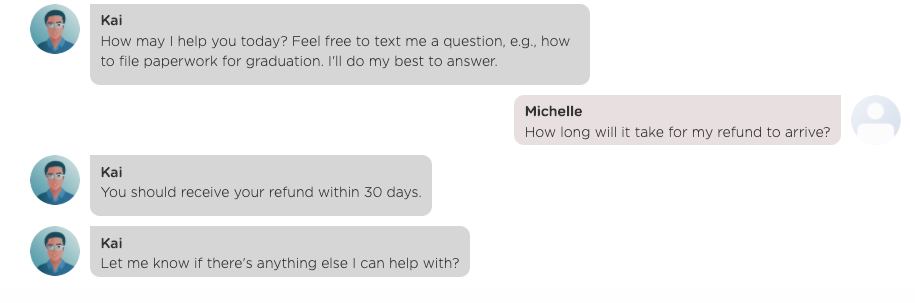
With true NLP capabilities, Juji chatbots can recognize semantically similar user questions in diverse expressions. For example, with the above entered Q&A pair (e.g., "When will I receive my refund"), the chatbot is able to answer a user question expressed very differently ("How long will take my refund to arrive") as shown below.
Second, if you have a long list of Q&A pairs already, you can download our CSV template and put them into a CSV file as shown below. The format of the CSV file is also explained in our online documentation.

Design helpful HELP command
Once you enable your chatbot to support free-text Q&A, it is always a good idea to write a helpful HELP command that can guide your users' interaction with the chatbot.
Similar to a restaurant menu, a HELP command can help achieve two goals:
- helps users get started especially if a user is new;
- teaches users your chatbot's capabilities and sets up the right user expectations.
Here are 3 quick tips on writing a good HELP command for your chatbot:
- Write a response that gives an overview of your chatbot
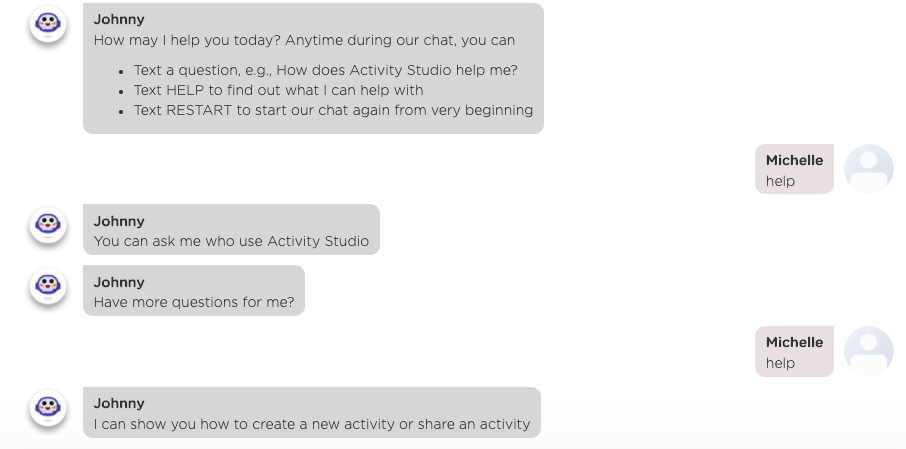
- Paraphrase HELP responses to expose different but specific chatbot functions (see the screenshot below)
- Make sure your chatbot does what it promises in its HELP command.
Satisfying the last point mentioned above is especially important to meet user expectations and deliver satisfactory user experience. In particular, you want to make sure the following conversation won't ever happen to your chatbot:
User: help
Chatbot: I can help you transfer money.
User: transfer money
Chatbot: I am sorry I don't understand you.
To prevent such user frustrations, you want to:
- carefully word the HELP command responses to anticipate and minimize possible user input variations; and
- handle potential user input variations that you can anticipate.
Convert website FAQs to Q&A entries
If you already have a webpage that includes FAQs about your business, you can also contact us and check if we could help you automatically convert these FAQs into the entries in a CSV file, saving your time and effort of preparing for the CSV file from scratch.
Step 2. Define multi-turn conversation flows to handle complex questions
Sometimes, a chatbot must engage with a user in a multi-turn conversation in order to answer the user's question. Consider the following example:
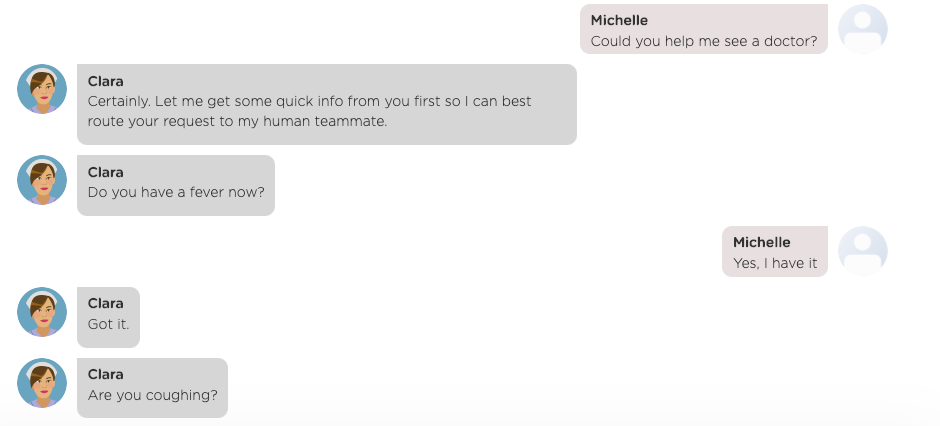
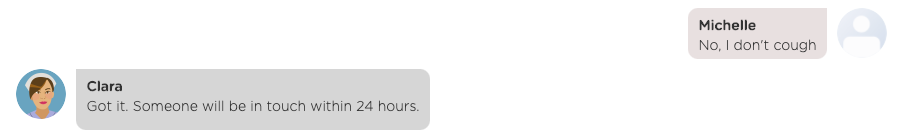
As shown above, the chatbot needs to collect basic information from the user first before answering the user's question.
To enable your chatbot to handle complex questions, Juji allows you to define a multi-turn conversation easily. In particular, you can define a mini chat flow that can elicit user information and use such information to decide how to best answer the user's question.
The screenshot below shows a chat flow defined to handle the user's request of seeing a doctor.
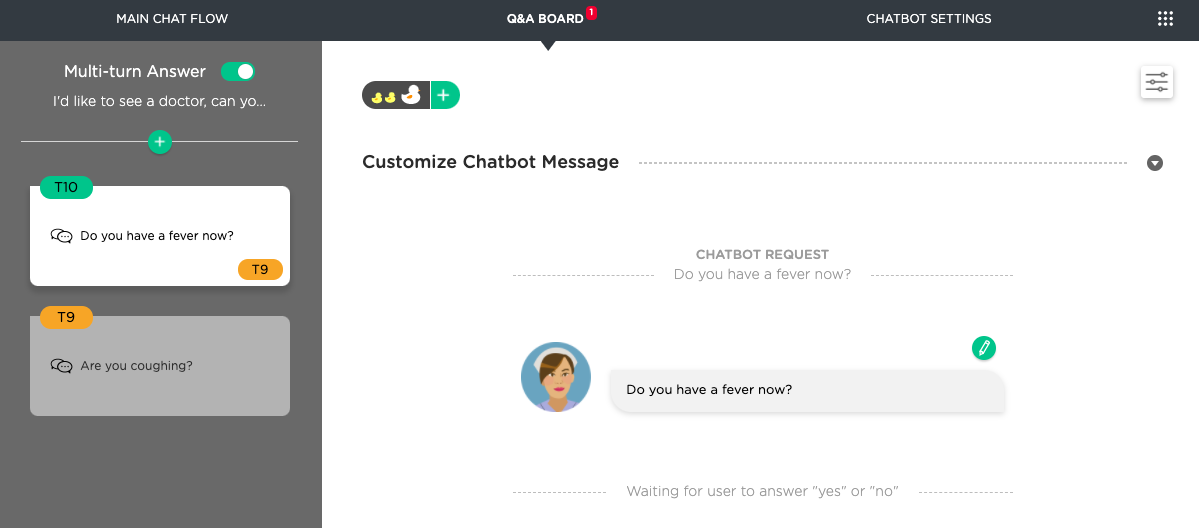
During such a multi-turn interaction flow, a user may interrupt the interaction flow with additional questions. For example, the chat flow below shows that the user asks a question about insurance before finishing up the thread on seeing a doctor.
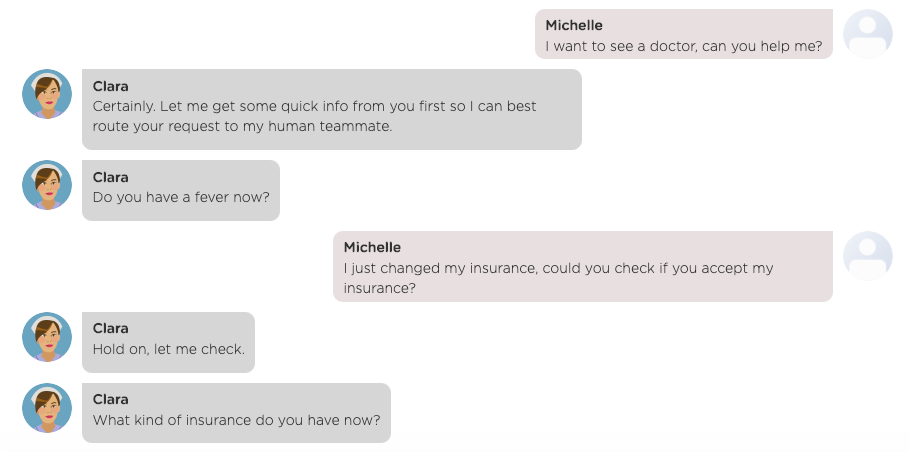
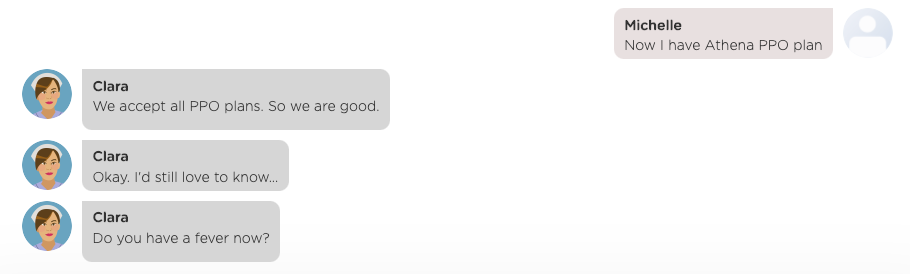
As you can imagine, a user can interrupt an ongoing chat flow and activates a new one anywhere, anytime. In other words, a chat flow can arbitrarily nest one or more other chat flows. Fortunately, Juji automatically manages all chat flows and keep track of the conversation context so you don't need to manually track the conversation context or wire different chat flows together.
Step 3. Monitor and improve customer service chatbot periodically
There are always questions that a chatbot does not understand and cannot answer. A good AI chatbot should be able to handle unknown user questions as well as notify human agents where a chatbot fails. To better help human agents, Juji provides a Q&A dashboard that lists unanswered user questions as shown below.
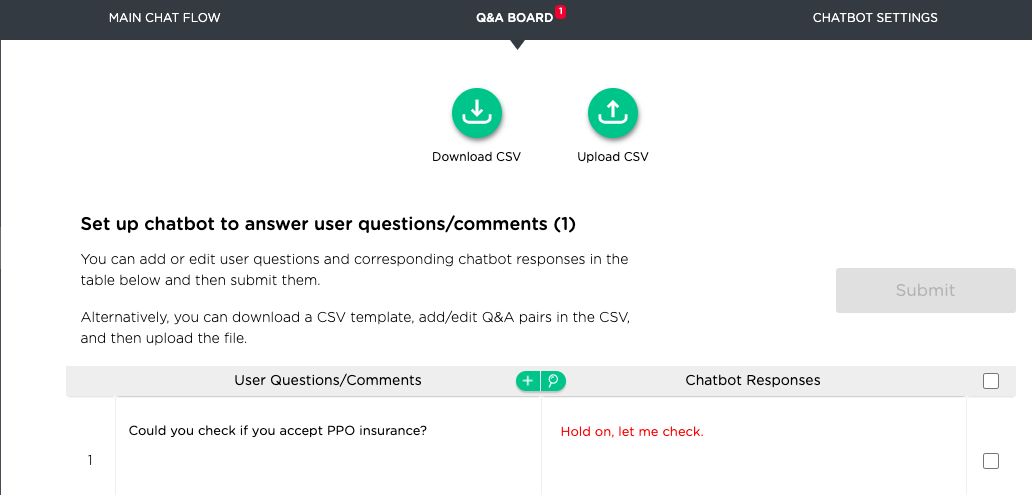
Whenever Juji detects an unanswered user question during a chat session, it lists the question on the Q&A dashboard. Juji also automatically suggests a potentially matched answer (as highlighted in red in the answer column above) if an unanswered user question is similar enough to an existing question in the knowledge base (e.g., exceeding a similarity threshold).
To keep a customer service chatbot up-to-date and improve the chatbot over time, we encourage a human agent or chatbot owner to check the Q&A dashboard periodically (e.g., once a day) and perform two actions:
- check the Q&A dashboard to verify the suggested answer or provide proper answer to each unanswered user question; and
- submit the Q&A pairs to update the chatbot
Once the the Q&A pairs are submitted, the chatbot is updated immediately and can answer similar questions in any ongoing chats.
How to Evaluate Customer Service Chatbot Platforms
As described above, Juji supports an easy 3-step process for an organization to build and upkeep a customer service chatbot with powerful AI capabilities and no coding required. Since chatbot platforms are abundant, in case you wish to compare different chatbot platforms before deciding on which one to use to build your customer service chatbot, we suggest that you evaluate a platform from four aspects to maximize your chatbot ROI:
Customer Service Quality. This is to measure how well a chatbot can serve your customers. Can the chatbot understand user questions in diverse natural language expressions on a wide range of topics? Can the chatbot handle complex user questions that require a multi-turn conversation? Can the chatbot handle arbitrary user interruptions occurred during a chat while still ensuring task completion?
Ideally, you want your chatbot to automatically handle at least 40% customer inquiries from the very start and gradually improve to handle over +70% customer service requests over 1-2 months. This will present over 60% savings on your customer service cost and infinite amounts of customer happiness.
Implementation Speed. This is to measure how fast you can set up a quality chatbot with full AI capabilities as discussed above to deliver satisfactory customer services. Ideally,
- for a small business with thousands of customers, the setup time should be within 1-2 days, not for weeks; and
- for a medium business with hundreds of thousands even millions of customers, the setup time should not exceed 1-2 weeks, definitely not months.
The speed to setup often reflects the effort required to upkeep your chatbot and eventually the ROI of your chatbot. If it would take months to set up an initial customer service chatbot, it is most likely that it will take weeks to make any changes in your chatbot. Another associated criterion is to know who needs to be involved in the chatbot setup and upkeeps. If everything requires the involvement of your IT team, it is a signal to a very costly solution with low ROI.
If it is difficult to keep a chatbot up to date, customers will then eventually abandon the chatbot and the chatbot investment will go down the drain.
Service Robustness and Handoff. This is to measure how well a chatbot can handle exceptions -- unknown user inquiries. No chatbot is perfect. You want a customer service chatbot to be resilient even under uncertainties, which directly impacts customer satisfaction.
For example, what does a chatbot do when it encounters unknown user questions or comments? Does it recommend similar questions and give users a chance to find the answers or simply reply with "sorry, I don't understand your question"?
Another consideration is how easy to support chatbot-human handoff. Human agents should be aware of chatbot failures, ideally all time and in real time so they can help resolve the issues promptly. To deliver exceptional customer experience, human agents should have sufficient information for the handoff, ideally understanding emotional state and unique characteristics of the customers involved beyond the issues to best serve the customers.
Chatbot Learnability. This is to measure how fast and easy a chatbot can be improved. Adopting a chatbot is like raising a child, you'll have to update the knowledge of a chatbot periodically to improve its performance. Selecting a platform that can help human agents to update a chatbot easily and quickly can greatly improve the ROI of a customer service chatbot.
From Customer Service to Customer Advocacy
Another criterion you may want to consider is how easy you can extend a customer service chatbot to becoming a customer advocacy chatbot. In addition to answering customer inquiries, a chatbot could also elicit customer reviews or gather user feedback about products and services in the same chat (see screenshots below).
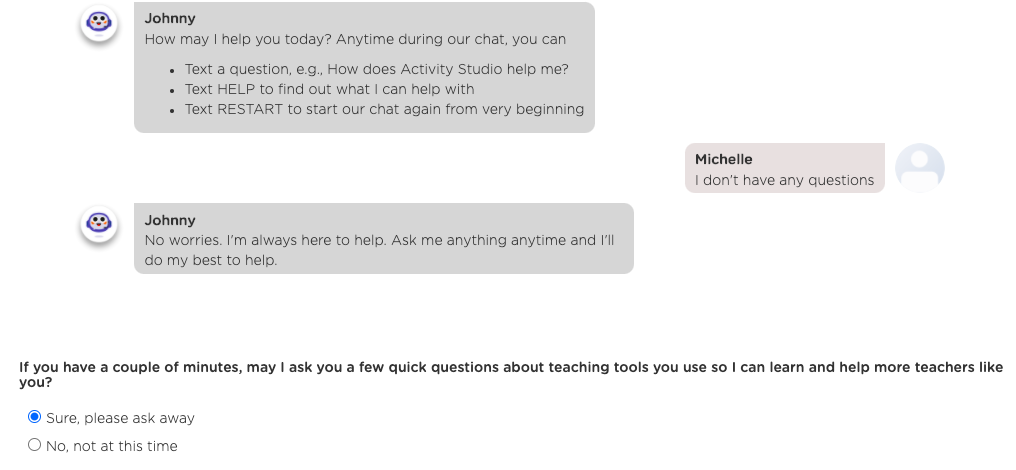
Juji allows you to do so easily without coding by adding a few conversation topics in the chatbot main flow. The added conversation can further improve the ROI of a customer service chatbot by automating more customer operations (e.g., product survey).
Further Readings
If you are considering a customer service chatbot for your organization, we hope you find this post helpful in your decision making process. Additionally, we encourage you to follow the three steps listed above to build a customer service chatbot on Juji (choosing the customer service template) and experience it yourself firsthand.
I also list several pieces of information you may find useful:
- How to set up a customer service chatbot with AI enabled. Here is a short Youtube video showing how to prepare your custom Q&As with no coding and a blog post describing the process in detail.
- How to set up multi-turn conversations to handle complex questions. Here is a short Youtube video on how to create multi-turn chat flows with no coding to handle complex questions and a blog post on detailing the process.
- How to monitor and update a customer service chatbot in real time. Here is a blog post detailing how the Juji Q&A dashboard works and helps human agents improve a chatbot instantly.
- How to learn unique characteristics including emotional signatures of a user from a chatbot conversation. See this article of ours. Such information can be used to help human agents best help each customer.