Recently, we have heard more people, especially top technology experts, talk about creating "proactive" AI agents with agentic workflows (e.g. see a recent video by Andrew Ng). Designing a proactive AI agent requires skills. In this article, we present 5 design tips for conversational AI designers to make effective proactive AI agents. In each design tip, we use concrete examples to explain the desired AI agent behavior and show the corresponding Juji features you can use to enable such a behavior.
Tip 1: Make an articulate AI agent
A proactive agent doesn’t just passively respond to user questions. Rather, it actively engages with a user and guides the user toward an agenda (e.g., tutoring the user to learn a skill or coaching the user on coming up with an individualized career development plan). During such an engagement, just like a good human agent, a proactive agent should be articulate in expressing itself, no matter whether it asks or answers a question. Below are two situations where a proactive agent should be articulate in making a conversation more natural and fluent.
(1) In many applications including interviewing and counseling, a proactive AI agent often needs to ask user questions to elicit necessary information before guiding the user toward a goal. Just like a human interviewer, an effective AI agent should be able to ask the SAME question in different ways depending on the context. The image below (Image 1.1) shows a conversation where an AI agent must repeat its question when the user didn't answer the question.

Humans will never re-ask the question using exactly the same expression. Neither should the AI agent. The next image (Image 1.2) shows that the AI agent re-asks the same question in an alternative expression, which makes the conversation much more natural.

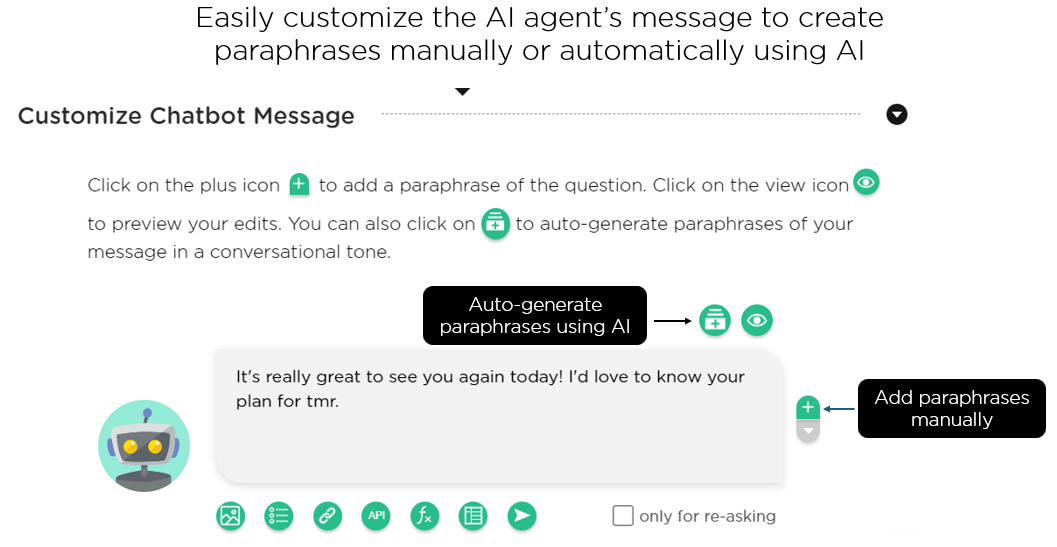
A conversational AI designer can use Juji Studio to customize an AI agent’s message, including paraphrasing a question either manually or automatically using generative AI (Image 1.3).
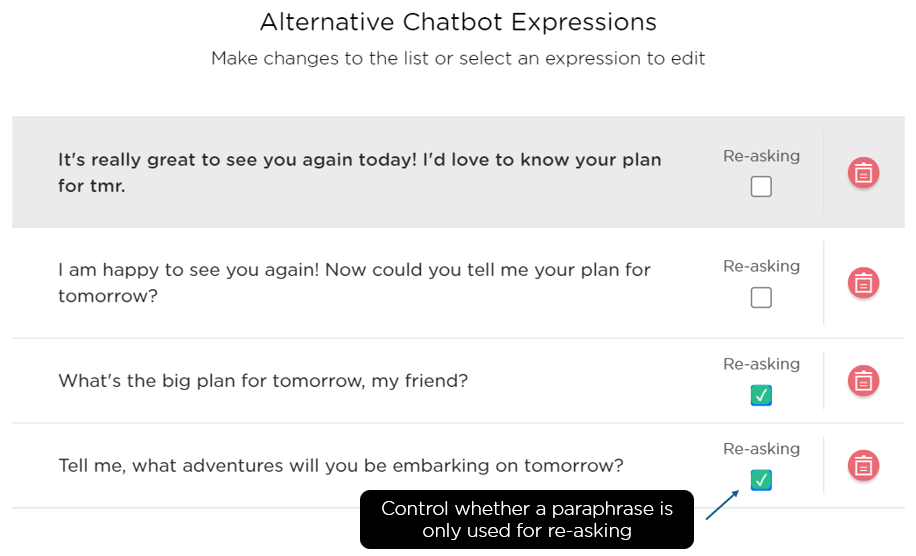
Furthermore, for each expression, a conversational AI designer can indicate whether it is only used for re-asking, giving you fine-grained control to make an AI agent articulate (Image 1.4).
(2) In a situation where a proactive AI agent must ask a series of questions to elicit information, the AI agent should also be able to ask these questions in a conversational tone and with smooth transitions from one question to the next, similar to what an articulate human interviewer would do.
In Juji Studio, conversational AI designers can use generative AI to auto-generate a conversation flow with multiple questions (Image 1.5), which you may edit with more human touch as needed.
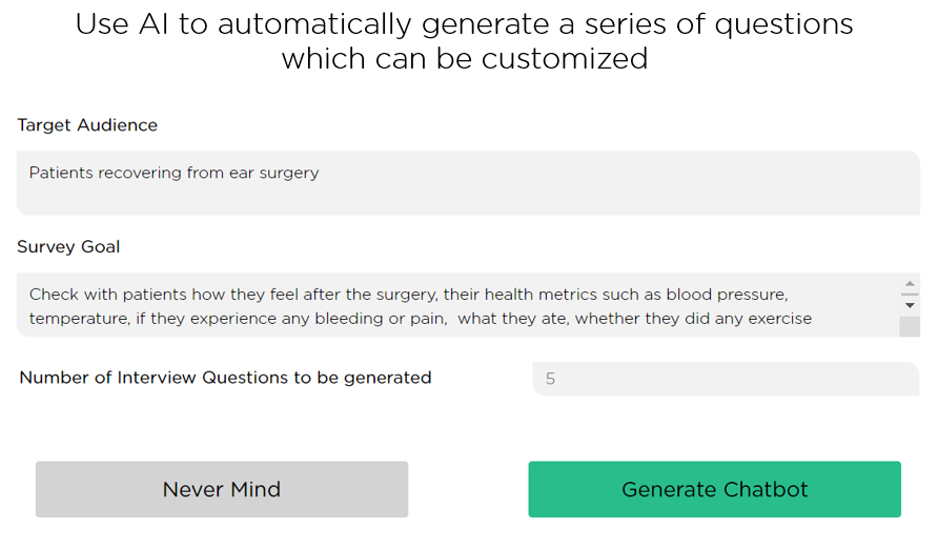
The result is a fluent conversation flow that resembles those of human-human conversations (Image 1.6).
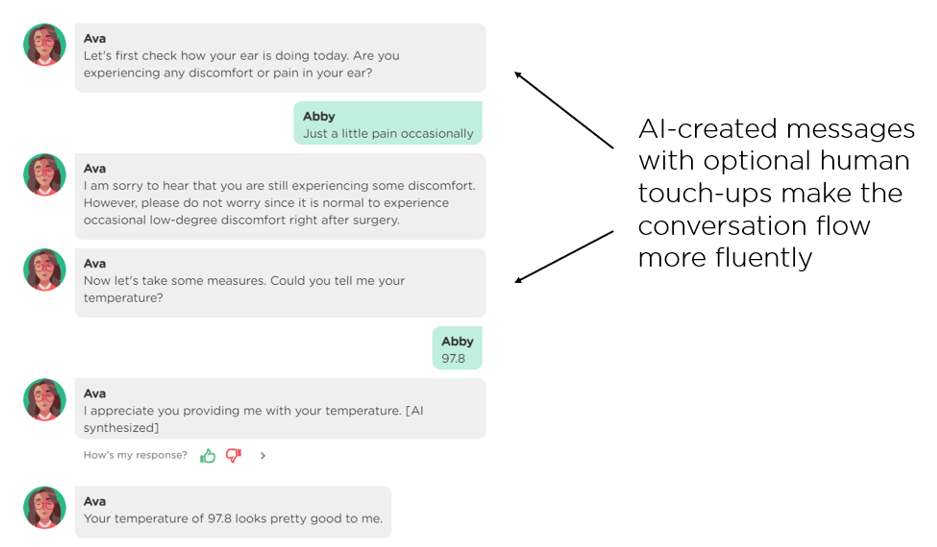
Tip 2: Make a well-prepared AI agent
Human conversations are highly diverse and rarely single threaded, which require active listening, empathy, and negotiation skills to keep a conversation going and achieve the intended communication goals. Just like a good human conversationalist, a proactive AI agent should also be well-prepared to handle diverse conversation situations gracefully. Below we list several frequent conversation situations where a proactive agent should be well-prepared to handle them.
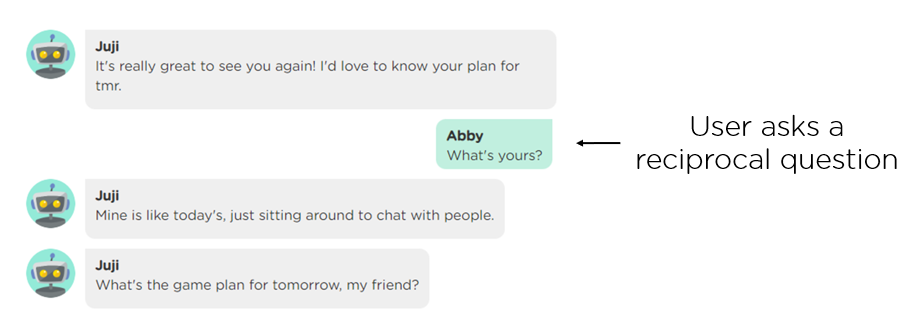
(1) Handle user reciprocal questions. In a human-human conversation, humans often ask reciprocal questions such as "What's yours" and "what about you". A well-prepared AI agent should also handle user reciprocal questions (Image 2.1).
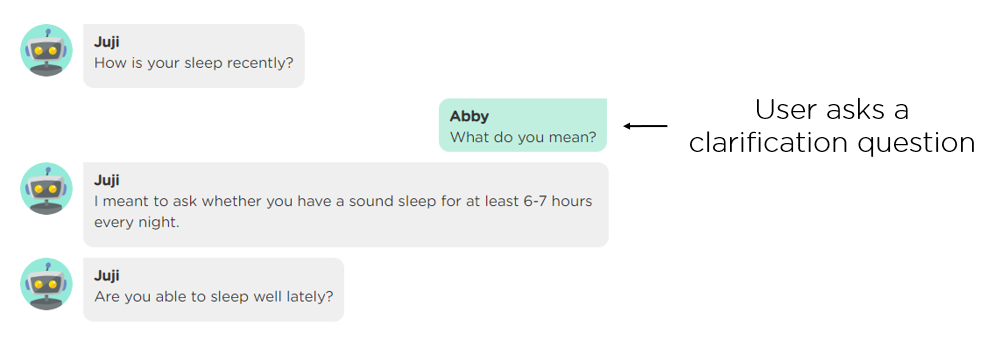
(2) Handle user clarification questions. Different people have different background and knowledge. A perfectly clear question to one person may be difficult for another to understand. So prepare your AI agent to answer user clarification questions during a conversation (Image 2.2).
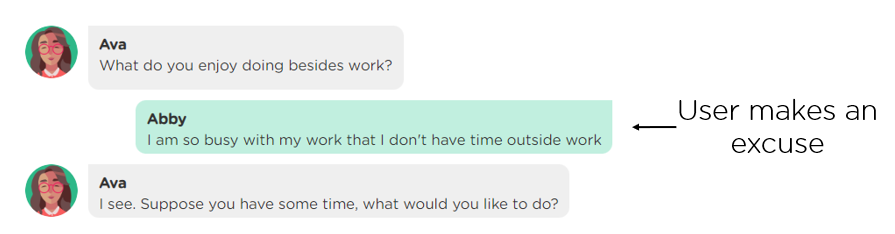
(3) Handle user excuses. Just like in human-human conversations, people may dodge a question by giving various excuses. A proactive AI agent should also be prepared to handle diverse user excuses to accomplish an agenda, e.g., eliciting quality information from a target audience (Image 2.3).
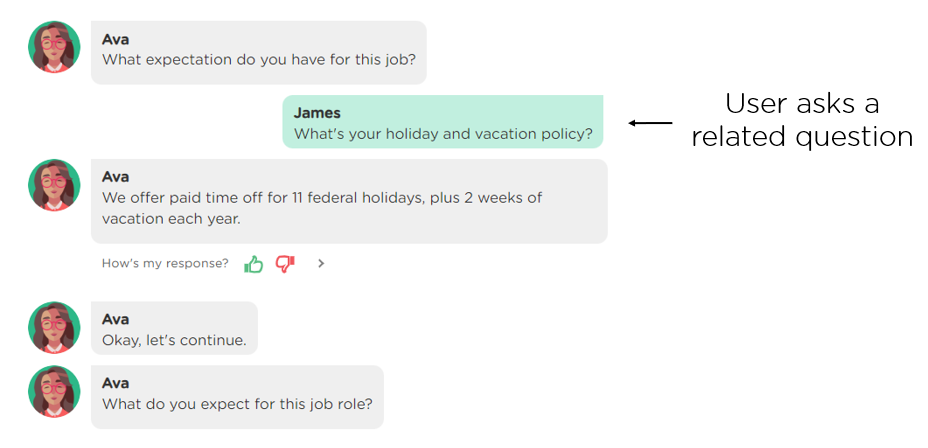
(4) Handle related user questions in context. During human-human conversations, people may ask relevant questions to a topic under discussion. A proactive AI agent should also anticipate relevant user questions and be prepared to answer the questions in a conversation (Image 2.4).
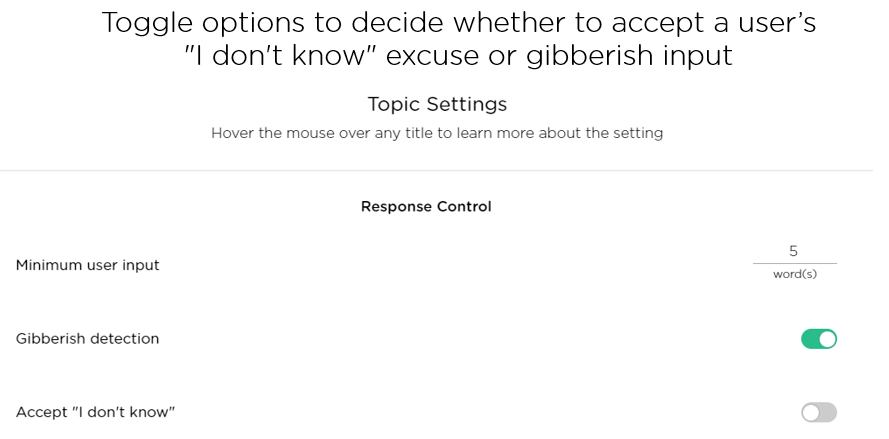
Feel overwhelmed that you have to handle all the above situations and don't know how? No worries, conversational AI designers can use Juji Studio to prepare an AI agent to handle all the situations mentioned effortlessly with 100% #NOCODE. For example, A designer can easily toggle options to decide whether to accept a user's "I don't know" excuse or gibberish input in a specific conversation topic (Image 2.5).
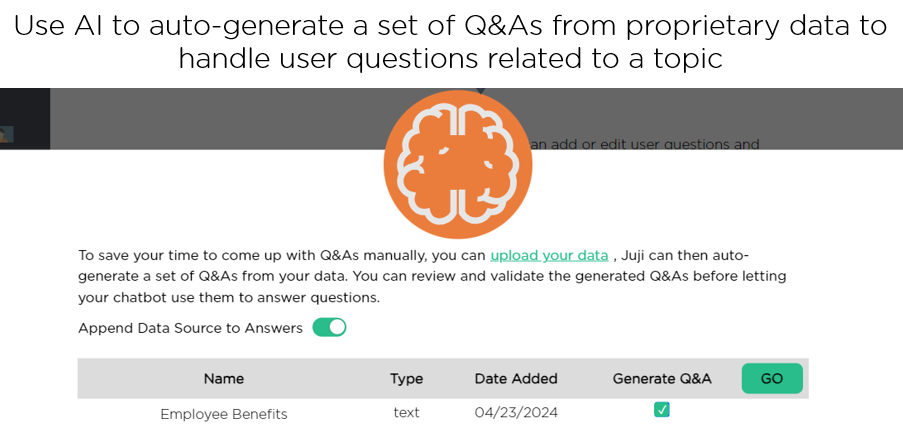
A designer can also upload one or more proprietary data and then ask Juji to generate a set of Q&As automatically to handle user questions related to a topic (Image 2.6).
Tip 3: Make a responsible AI agent
Every AI agent is designed with a purpose. A proactive AI agent must act responsibly to ensure task completion and goal fulfillment. So how can conversational AI designers instill a sense of responsibility into an AI agent? From our own experiences, we have found there are at least three types of responsibility that a proactive AI Agent should have.
(1) Ask follow-up questions to deepen a conversation and accomplish the goal. In many applications such as interviewing and counseling, a proactive AI agent typically asks open-ended questions to elicit richer information. However, users may not cooperate and instead provide overly general or vague information. In such a situation, a responsible AI agent should ask follow-up questions to deepen the conversation, ensuring that relevant details are gathered. The two images below (Image 3.1 and Image 3.2) show an example where the AI agent automatically generates follow-up questions to elicit must-have and nice-to-have information based on the user's responses.
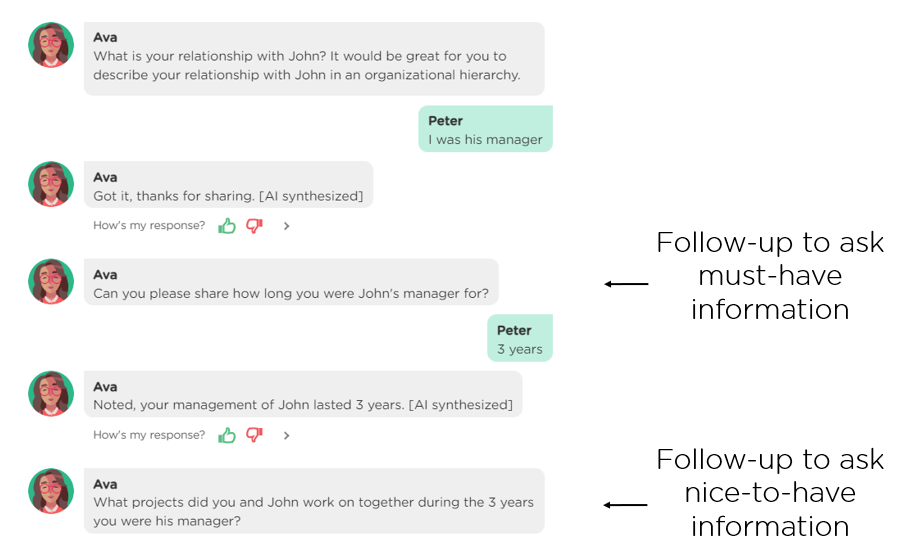
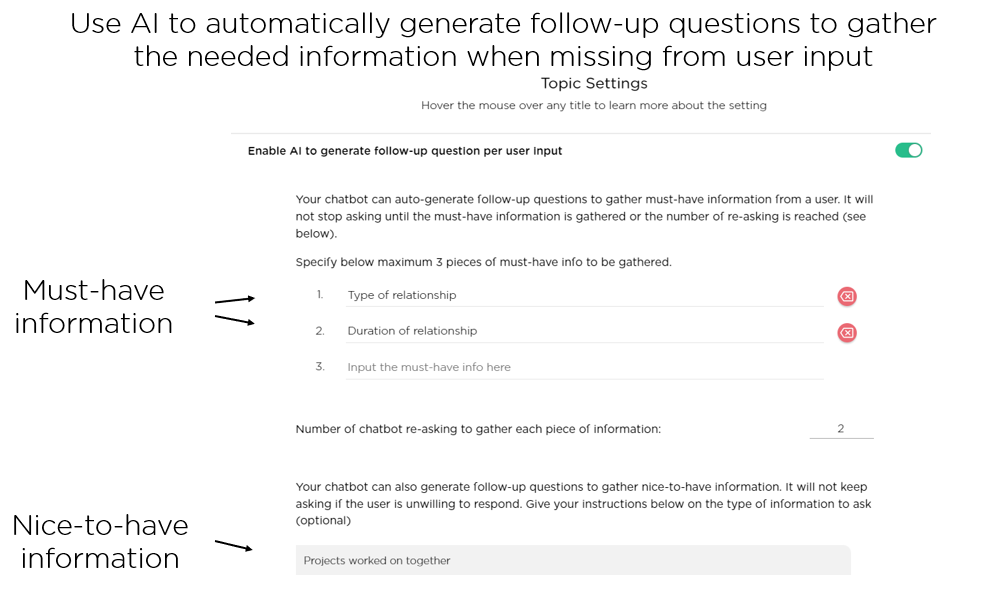
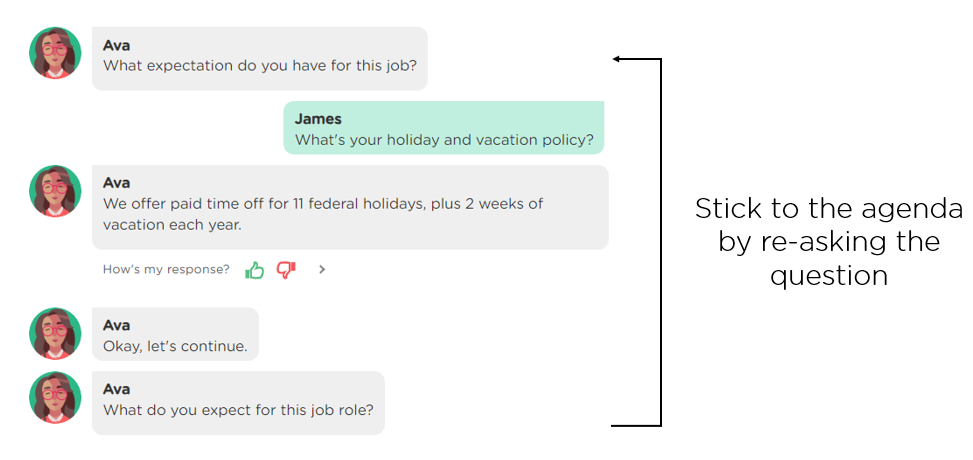
(2) Stick to an agenda for task completion. Every proactive AI agent should have an agenda (aka workflow) that drives the conversation toward task completion. However, most conversations often digress. A responsible AI agent should manage the digressions/distractions and stick to the agenda. The following image (Image 3.3) provides an example of a conversation where the AI agent handles a user digression gracefully and then goes back to the agenda. Conversational AI designers don't need to do anything but directly leverage Juji Studio's built-in capabilities for AI agents to stick to their agenda automatically.
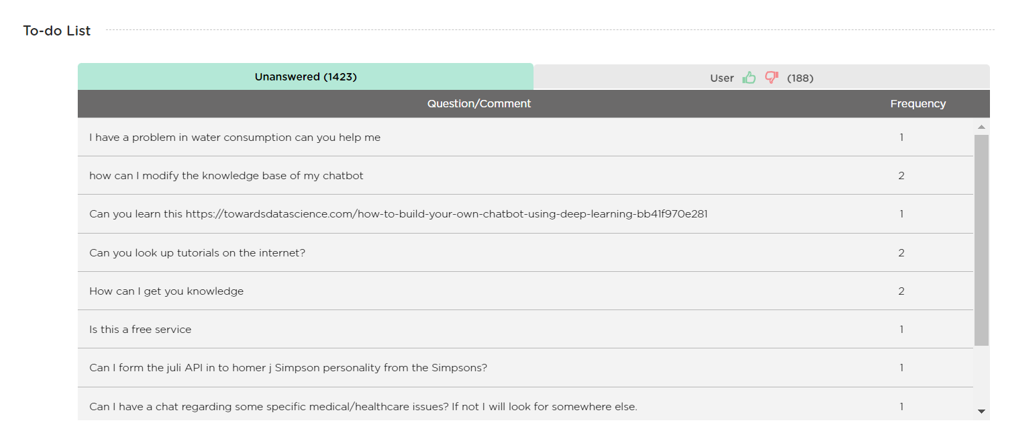
(3) Be a good human collaborator. AI is far from perfect. There will always be questions that an AI agent can’t answer or tasks it can’t complete. A responsible AI agent should collaborate with human teammates when necessary. For example, the image below (Image 3.4) shows the interface in Juji Studio where an AI agent flags unanswered questions or unfinished tasks in a to-do list for humans to review and to improve the AI agent's performance over time.
Tip 4: Make a perceptive AI agent
Effective human communicators have great social-emotional intelligence in addition to their language skills. In other words, they can read people during a conversation and use the reading to empathize with their conversation partners and foster effective and pleasant conversations. Similarly, a proactive AI agent should be perceptive and possess the ability to actively listen to its users, infer the users' unspoken needs and wants from a conversation, and personalize each interaction. Such capability enables AI agents to better help their users based on each user's unique needs and wants. Here are two conversational design tips to power a perceptive AI agent.
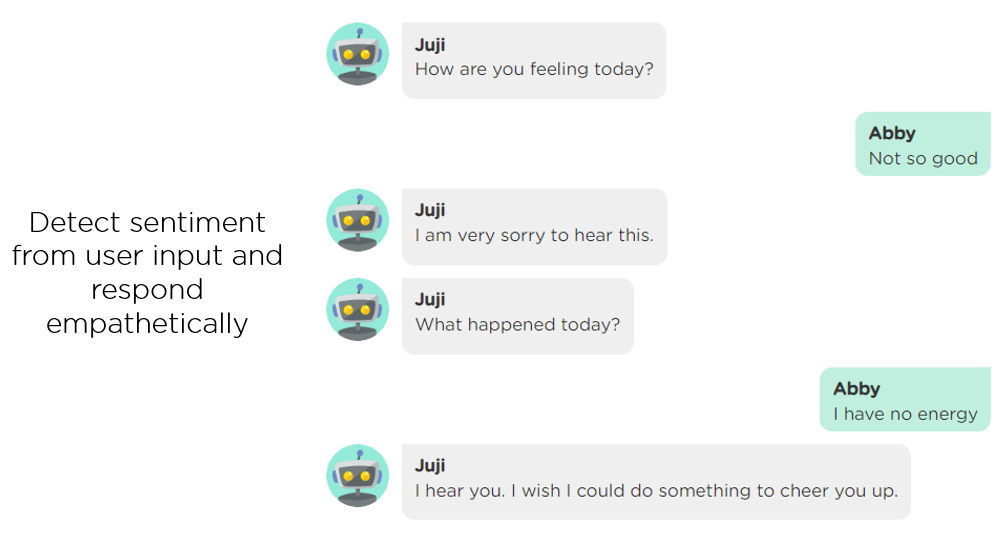
(1) Enable an AI agent to read user emotions. A perceptive AI agent should actively listen to its users, echo their sentiments and recognize their feelings. This makes users feel heard and understood. The following image (Image 4.1) gives an example of an AI agent detecting sentiment from the user’s input and responding empathetically.
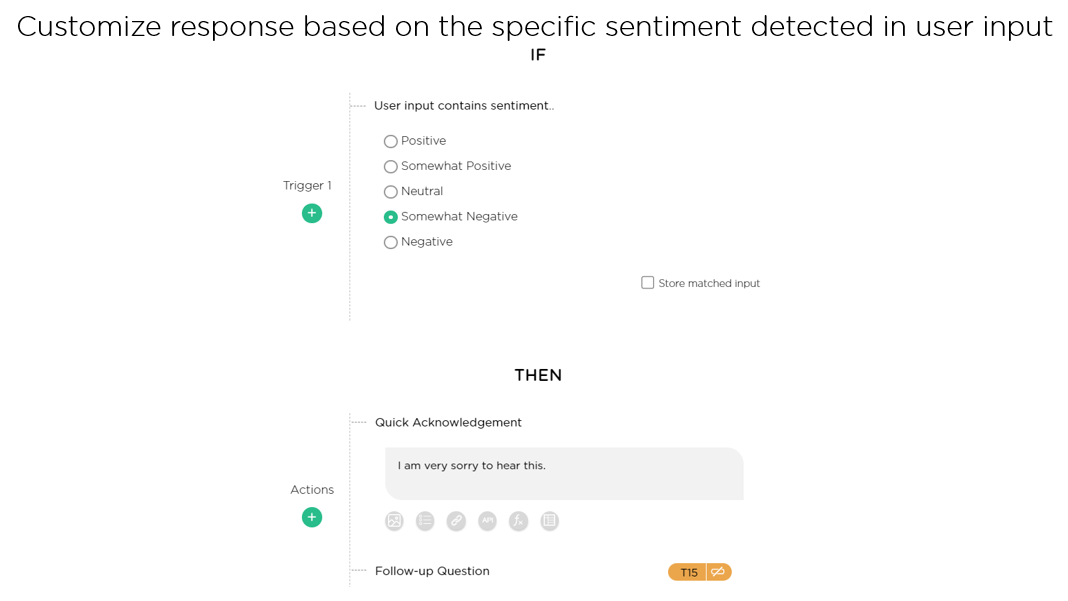
The image below (Image 4.2) shows how a conversational AI designer can easily customize the AI agent’s response in Juji Studio based on specific user sentiment detected during the conversation.
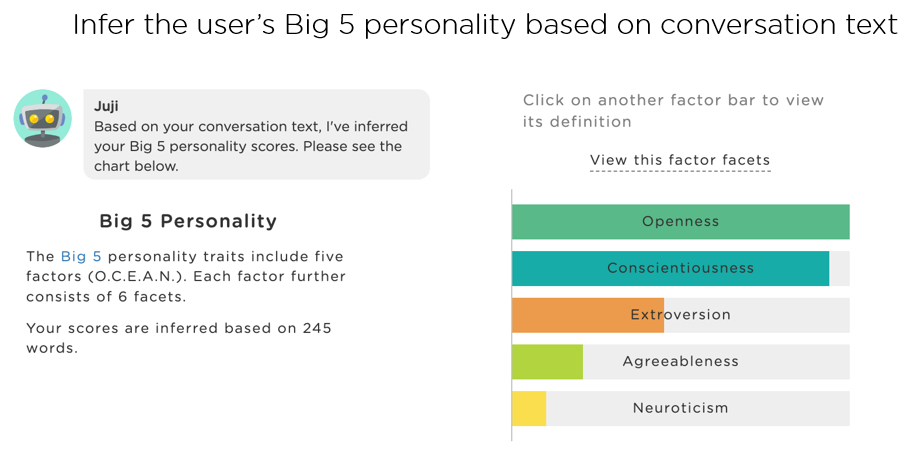
(2) Enable an AI agent to read user personality. A perceptive AI agent should also read between the lines in a user engagement to deeply understand each user’s unique characteristics, including his/her motivations, interests, needs, and personality. The image beneath (Image 4.3) shows how an AI agent is able to infer a user's Big 5 personality traits from their conversation. Conversational AI designers can leverage Juji Studio to detect AI-inferred user personality and generate messages based on user personality.
Tip 5: Make an adaptive AI agent
A skilled human communicator adapts each conversation to their conversation partners, making the engagements more effective. Likewise, a proactive AI agent should adapt its engagement to each of its users based on the user's background, interests, and personality. Below are two common types of adaptation that should be enabled to make an adaptive AI agent.
(1) Tailor AI agent explanations to suit an individual’s background, interests, and level of expertise to make the content more relatable and easier to understand. One of the important tasks for a proactive AI agent is to tutor students on complex concepts. If an AI agent can provide detailed explanations using terminology, analogies, and examples that each student is familiar with, it facilitates learning. The image below (Image 5.1) shows an example of an AI tutor that dynamically adapts blockchain tutorial content for a student who loves to cook.

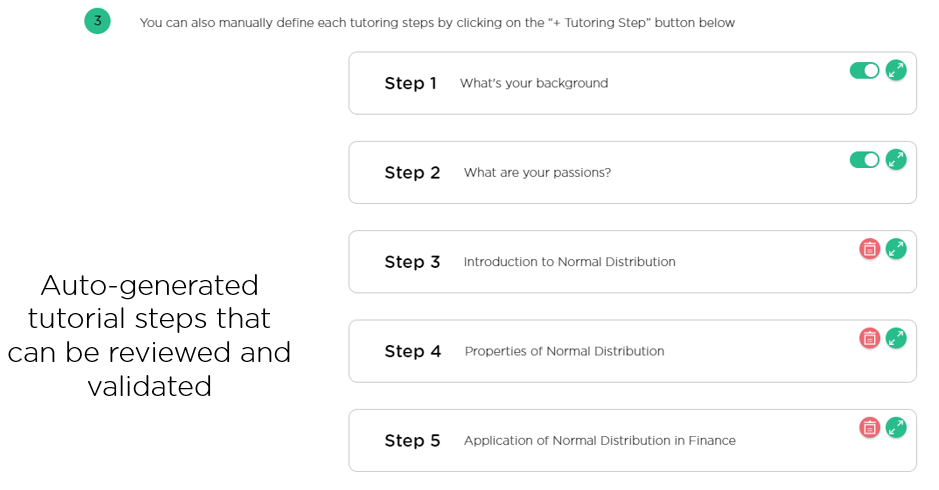
Conversational AI designers can leverage Juji Studio to auto-generate an interactive tutorial from proprietary data (Image 5.2)
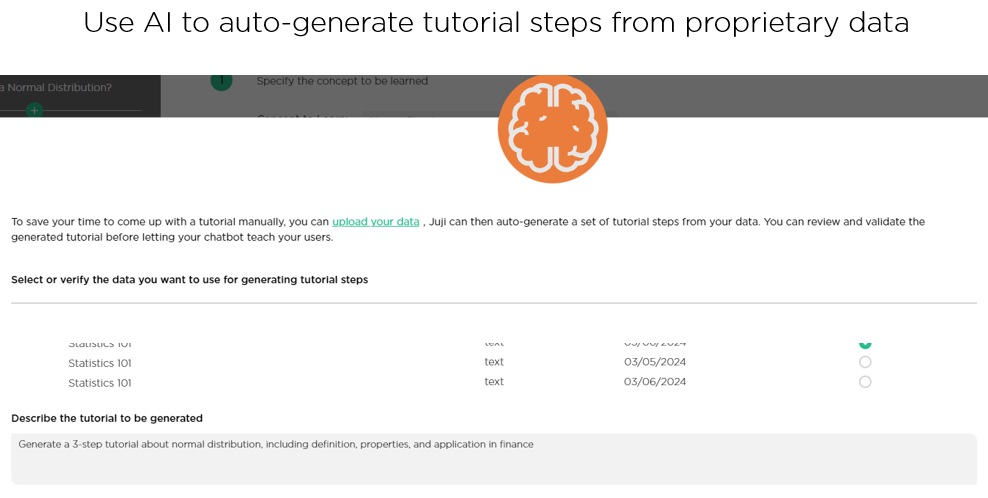
The designers can also review and revise the steps as needed (Image 5.3). During runtime, Juji’s AI agent dynamically tailors the content in each step of the tutorial to suit the user’s background and interests.
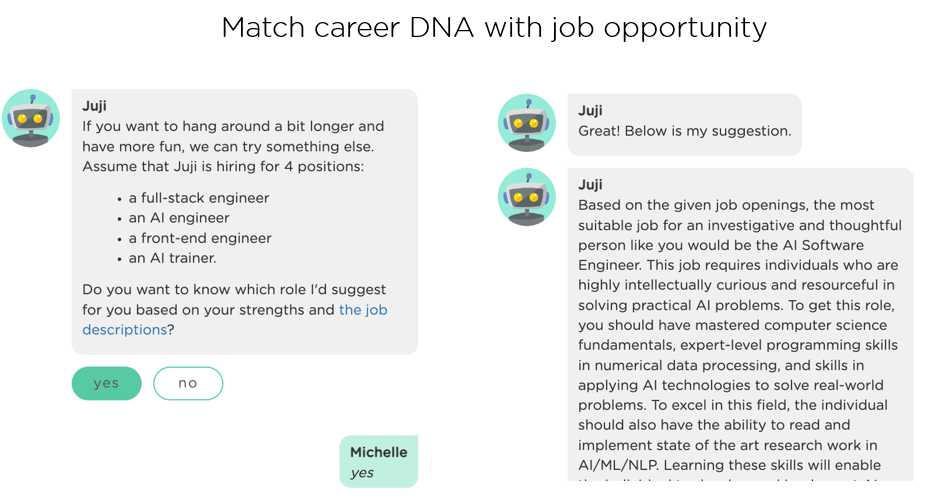
(2) Adapt suggestions/persuasions/guidance based on a person’s personality traits. Everyone is unique. If an AI agent can provide suggestions or guidance that can better resonate with each user based on their unique motivations, needs, and interests, it is more likely the user will follow the suggestions or guidance. The following image (Image 5.4) shows an adaptive AI career assistant that suggests a suitable job opening along with the required skills based on the user's goal, personality, and available job roles.
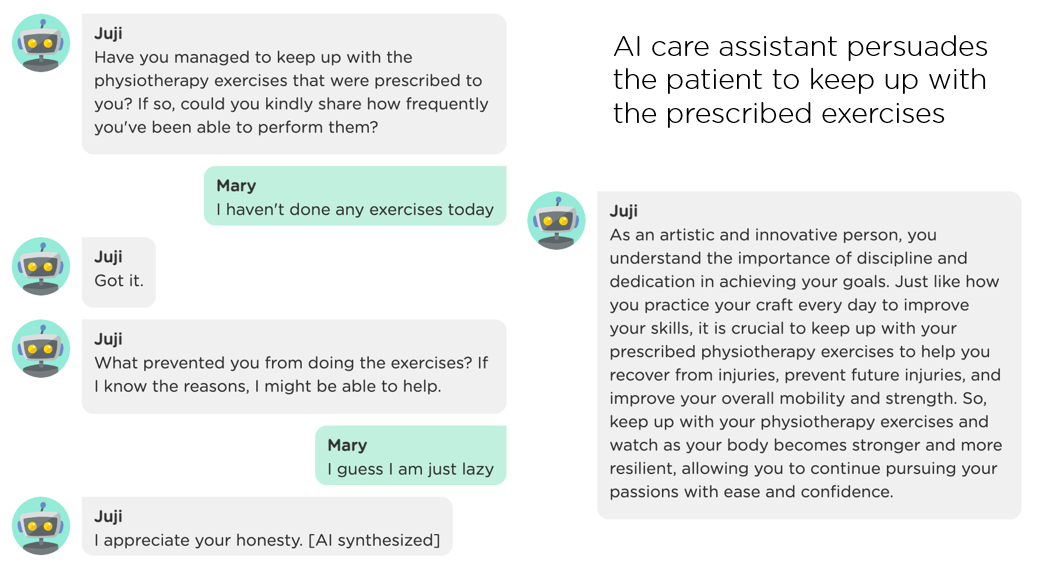
The next image (Image 5.5) shows an adaptive AI care assistant that motivates and persuades a patient to adhere to care routines with stories generated based on the patient's personality so the patient can easily relate to and be motivated by.
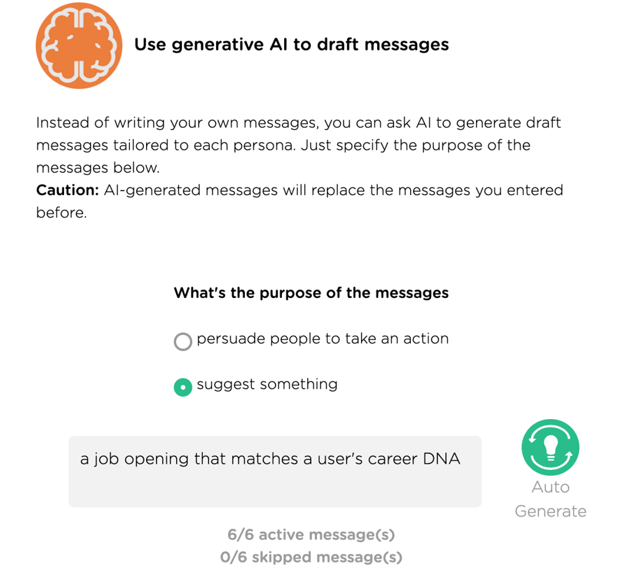
With Juji Studio, conversional AI designers can easily enable an AI agent to generate personalized messages based on Juji inferred user personality insights (Image 5.6).
In summary, we present 5 design tips for conversational AI designers to make proactive AI agents articulate, well-prepared, responsible, perceptive, and adaptive. Juji Studio makes it easy to create such an AI agent. Sign up to create your own and put those tips to use!