Are you considering an AI chatbot for your business? A simple Google search will present you with hundreds if not thousands of AI chatbot platforms! Almost all of them claim that they are powered by generative AI and all seem to offer similar features, giving the first impression that any of them would do the job.
In reality, not every chatbot platform is created equal or is a perfect fit for the tasks you have at hand. For example, many of our customers mentioned to us before they found Juji, they had explored 20+ chatbot platforms but failed to find the one that meets their needs.
To help you expedite your chatbot platform selection process, in this article we will first identify different types of chatbots based on business needs, and then dive into each type of chatbot, listing the relevant key technical and business factors you should consider when evaluating different AI chatbot platforms for supporting that specific type of chatbot.
Identify the type of chatbot based on your business needs
First of all, business needs dictate which type of chatbot is needed.
To select a chatbot platform, the very first step is to understand why you need a chatbot and the expected tasks to be performed by the chatbot. You can then identify the type of chatbot that is needed. Based on the main tasks to be accomplished, chatbots can be roughly categorized into three types:
1. Question-Answering Chatbots (QA Chatbots)
The main task for these chatbots is to answer user questions based on public and/or proprietary information. For example, universities may use a chatbot on their website to answer student questions about learning programs (see Image 1.1 below), or hospitals may use a chatbot in their mobile app to answer patient questions on medical services. Very similar to the behavior of ChatGPT, this type of chatbot is typically driven by user questions and assumes that all questions can be answered in a SINGLE response, which is not the case in many real-world applications.

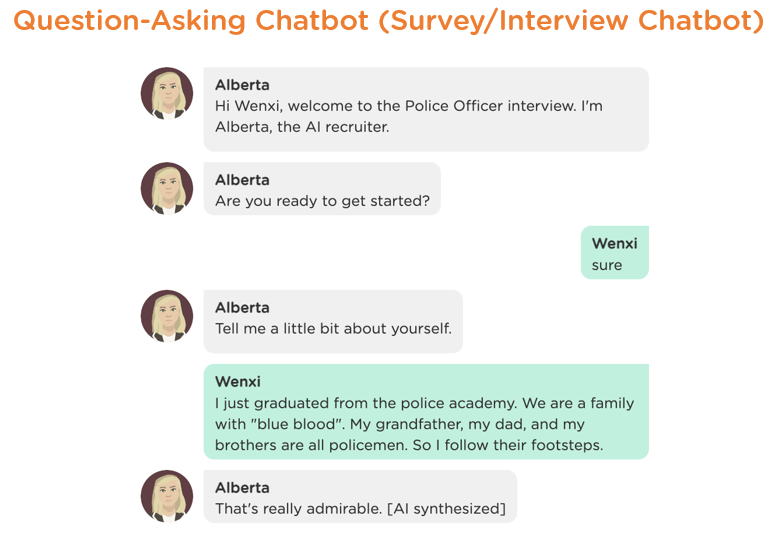
2. Question-Asking Chatbots (Survey/Interview Chatbots)
The main task for these chatbots is to ask user questions and gather information from an intended audience. Very similar to an online survey, this type of chatbot has been used to gather information for research studies, personality assessments, and job interviews (Image 1.2 provides an example of an interview chatbot). Typically, this type of chatbot is NOT capable of answering user questions including clarification questions during the process.
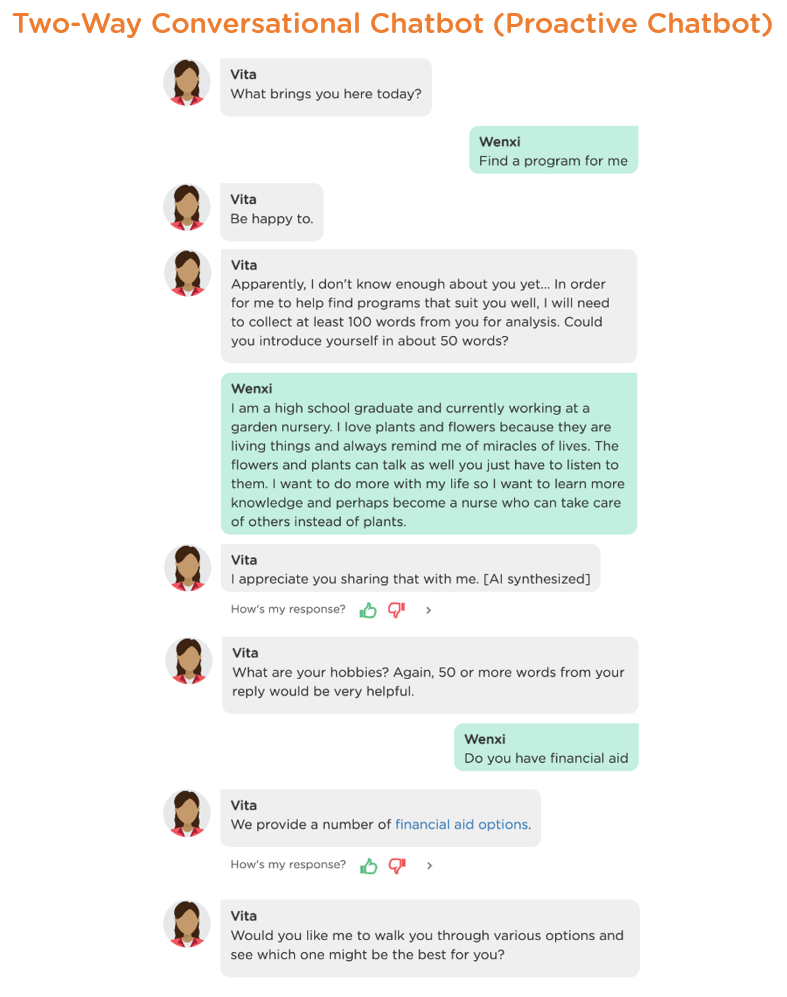
3. Proactive, Two-Way Conversational Chatbots (Proactive Chatbots)
In real-world applications, chatbots often need to perform multiple tasks simultaneously to deliver desired user experience and accomplish the business objectives. For example, a QA-only chatbot on a university website may be inadequate because the same chatbot must also ask questions to gather necessary information from the visitors before it can answer their questions (see Image 1.3 below). Similarly, a survey-only chatbot for job interviews may be unsatisfactory because it must also answer candidate questions regarding the positions and the organization during the interview. This third type of chatbot is a hybrid of the QA and survey chatbots, capable of both asking and answering questions during a conversation, known as Proactive Chatbots.
Building QA Chatbots
Here we outline 3 key factors to consider when selecting an AI chatbot platform to build a Question-Answering Chatbot (QA Chatbot).
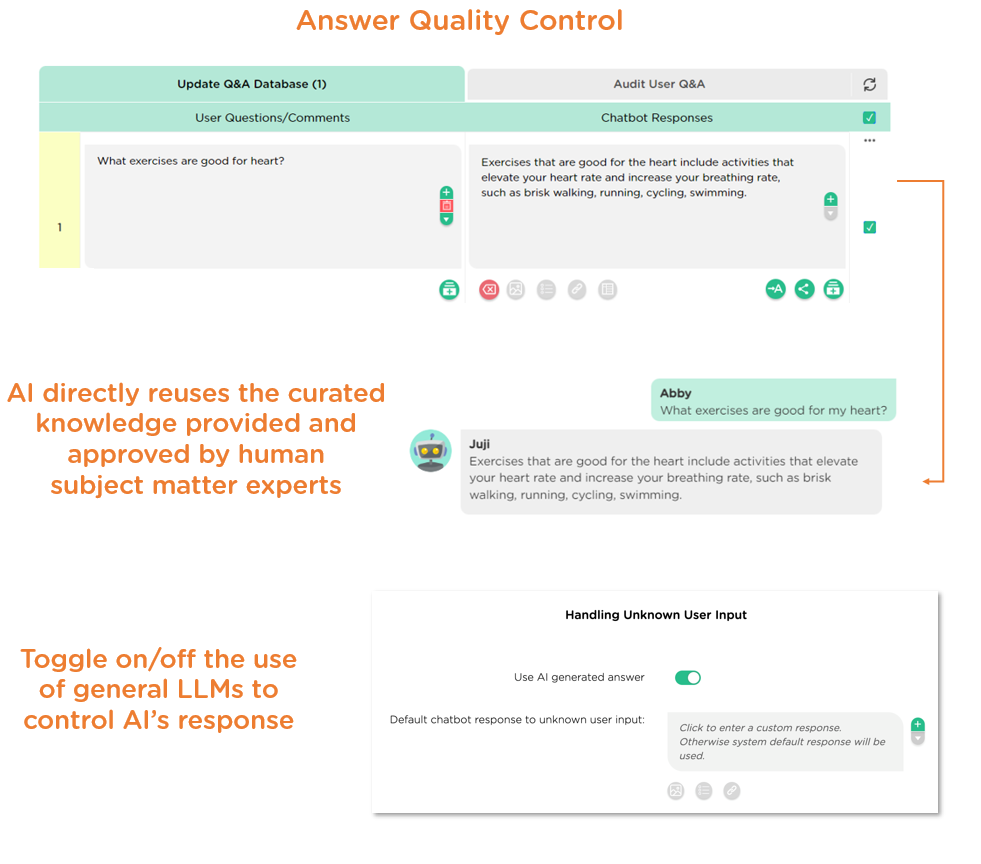
Answer quality and quality control
A QA chatbot's main job is to answer user questions. When evaluating an AI chatbot platform, the first factor is to evaluate how well the platform enables a chatbot to answer user questions accurately with no or minimum AI hallucinations. Unfortunately, the direct use of generative AI technologies, like Large Language Models (LLMs) and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), can't always guarantee high-quality AI responses because of their probabilistic nature. Therefore, ask the following questions during evaluation:
- How does your AI platform ensure the quality of AI responses, e.g., avoiding AI hallucinations?
- What kind of control measures can humans use to fine-tune AI responses (see examples in Image 2.1 below)?
Handling complex Q&A
Most AI chatbots powered by generative AI can answer simple questions—questions that can be answered with a single response. However, if your business requires a chatbot to handle complex user questions, it is important to evaluate how well an AI chatbot platform can support complex Q&A. In particular, ask the following questions during the evaluation:
- Can your AI platform handle complex Q&A, which involves multi-step interactions between a chatbot and a user (see Image 2.2 below for an example)?
- Who will define and manage the complex Q&A and how? For example, during a complex Q&A, the user may trigger another complex or simple Q&A, how will it be handled?
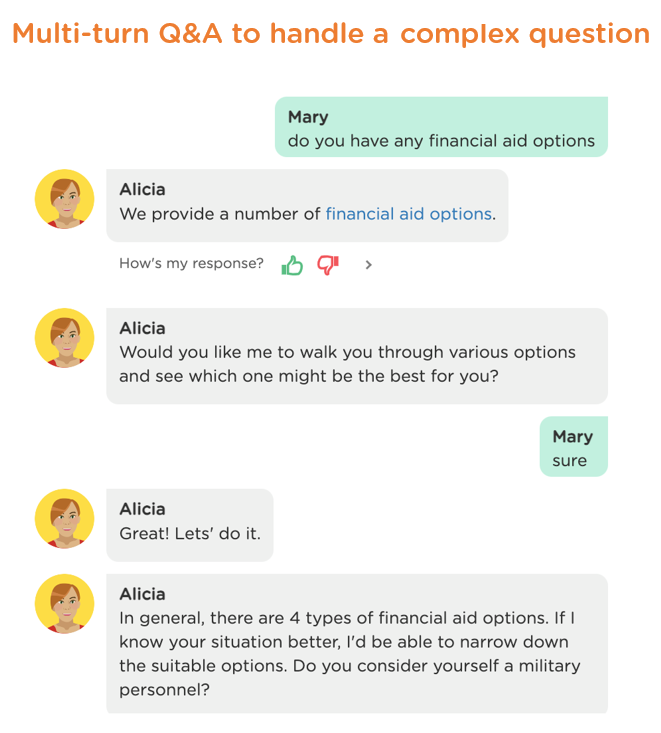
Handling complex Q&A is a very difficult problem. So you want an AI platform that is capable of handling various complex Q&A flows automatically.
Real-time chatbot Q&A monitoring and improvements
AI is far from perfect. When evaluating an AI chatbot platform, you want built-in tools that can monitor your chatbot behavior in real time, alert you with missed or problematic Q&As, and you can improve the chatbot in real time without interrupting any ongoing conversations (read more on this aspect at https://juji.io/blog/q-a-dashboard/
Building Survey/Interview Chatbots
Building an effective chatbot to ask questions and conduct surveys or interviews requires much more than just compiling a list of questions. Here are 3 critical factors to consider when selecting an AI platform to build a survey/interview chatbot:
Abilities to elicit quality user responses
The main task of a survey/interview chatbot is to gather quality responses from target users. When evaluating an AI platform, it is important to look for the following abilities:
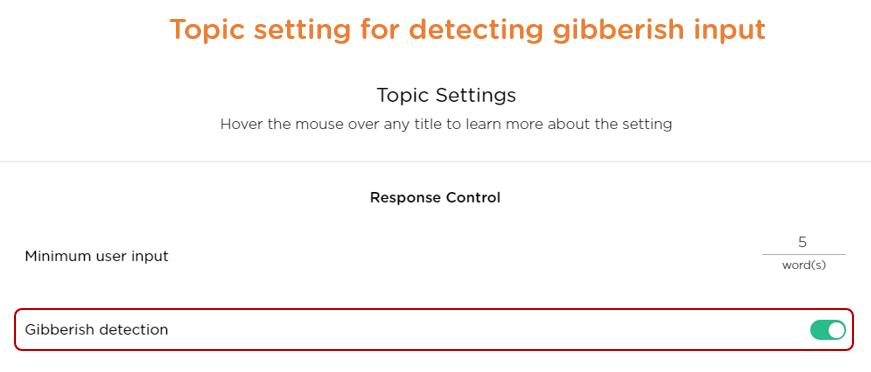
- Handling users' irrelevant, nonsense responses. An effective chatbot should recognize user responses that are off-topic or gibberish (Image 3.1), and prompt the user for a more relevant answer.
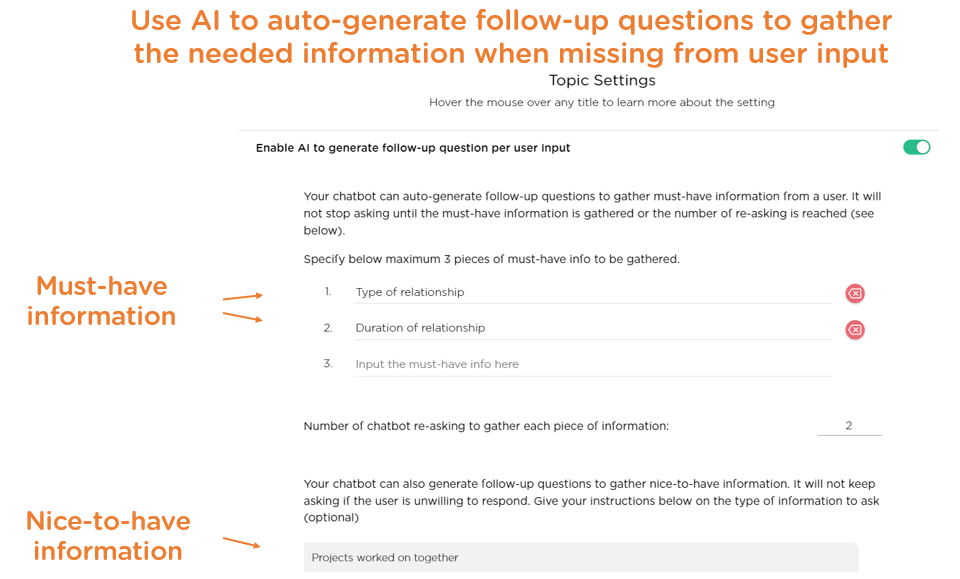
- Managing users' vague or brief responses with follow-up questions. To elicit quality responses, an interview chatbot should do what a human interviewer would: ask follow-up questions to drill-down to details if user responses are vague or brief (Images 3.2-3.3 show how to instruct follow-up question generation and examples of the follow-up questions generated).

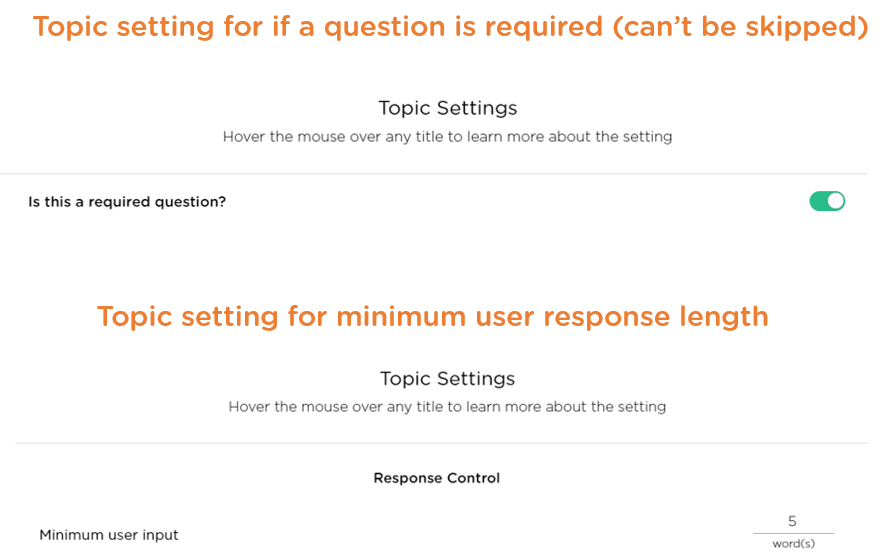
- Question configuration: Not all survey/interview questions are equal: some are to establish rapport, some are required, and some are not. Just like a good survey platform, a good AI platform should allow a chatbot designer to configure each chatbot question, e.g., whether a question is required (Image 3.4).
Abilities to handle user digressions
Each person has their own unique way of thinking and conversing. Even when there's a set agenda, human-to-human conversations rarely follow it precisely. The same goes for AI-human interviews. Therefore, your AI chatbot should be able to handle diverse digression situations, to bring the conversation back on track and successfully complete a survey/interview.
Since handling diverse types of digressions requires considerable effort, look for an AI platform that offers automatic, configurable digression handling (Image 3.5), accelerating time-to-value and AI ROI.

Abilities to generate survey/interview summary reports and analytics
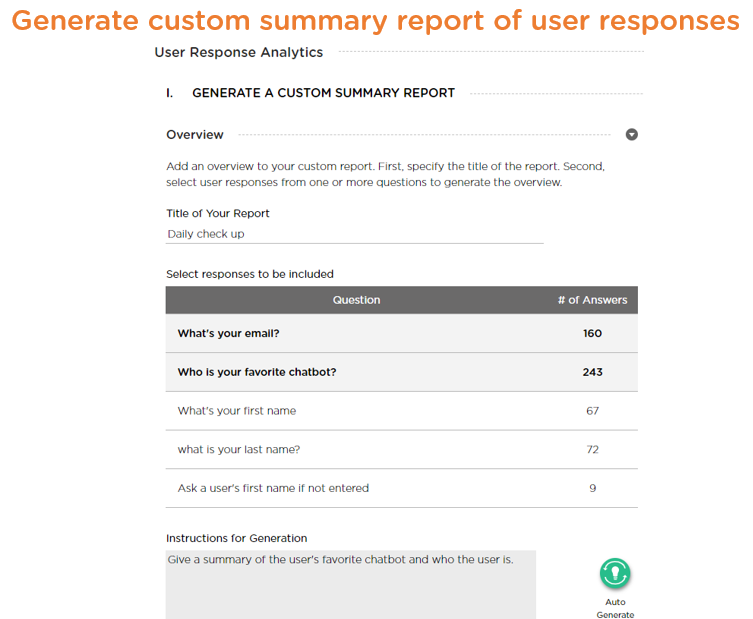
It's time consuming to wade through hundreds or thousands of chat transcripts and distill interview insights. When looking for an AI platform to build interview/survey chatbots, you want a platform that can also generate interview insights for fast and easier consumption, e.g., graphs and charts to illustrate trends and patterns of quantitative responses and summary of free-text responses (Image 3.6).
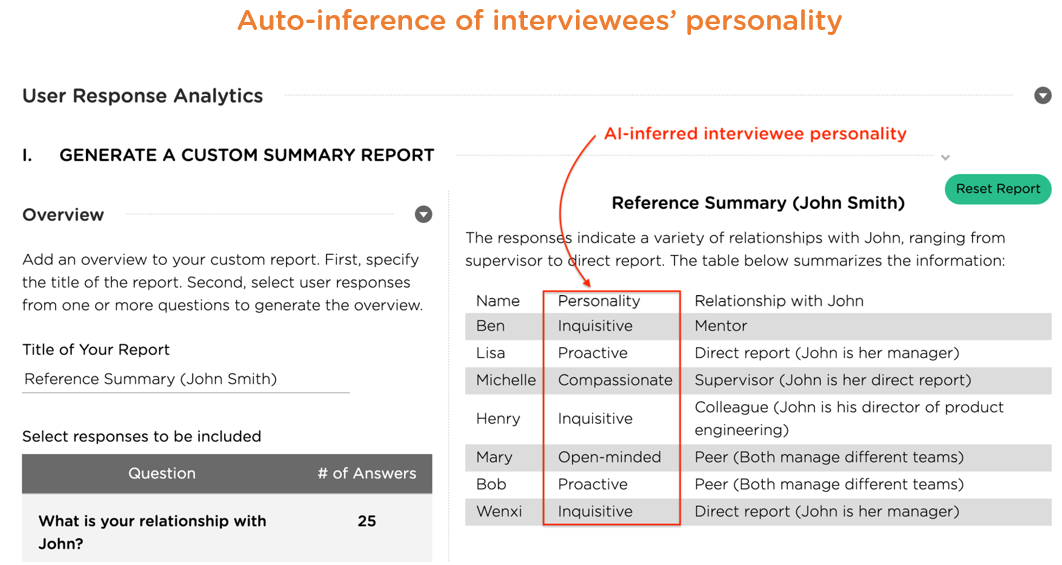
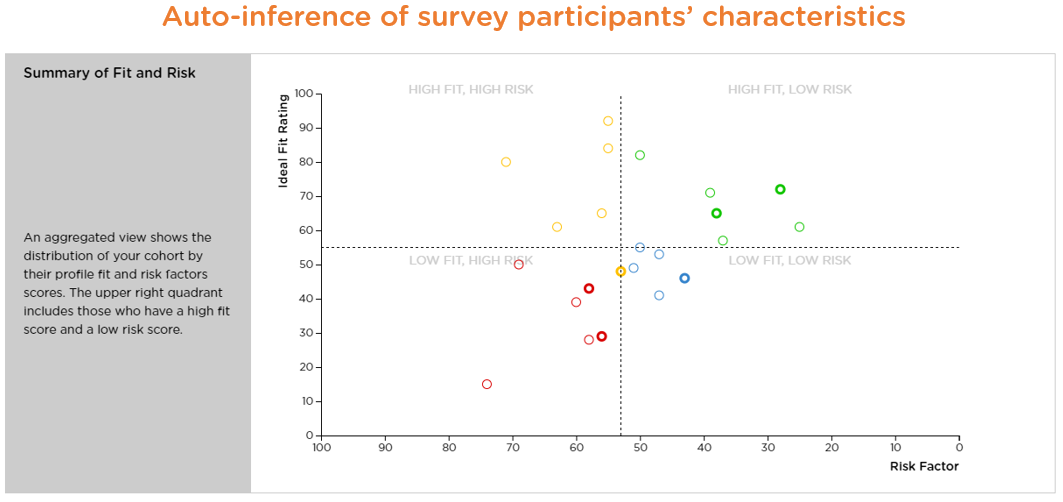
Additionally, an AI platform is much more desirable if it can automatically infer and analyze characteristics of survey/interview participants, which can deepen interview insights, such as reliability of the responses (see Images 3.7-3.8 for inferred characteristics of interview/survey participants).
Building Proactive Chatbots
Unlike QA-only and survey-only chatbots, proactive chatbots support two-way AI-human conversations, both asking and answering user questions during a chat. They typically are used to automate complex task flows that handle the interleaving of multiple, smaller tasks, such as answering a user's questions in the middle of interviewing the user. These chatbots are essential for automating and scaling services that involve high-touch, complex personal interactions (see the blog on this topic at https://juji.io/blog/do-you-really-need-an-ai-chatbot-use-these-3-questions-to-decide/). Since proactive chatbots are a hybrid of QA chatbots and survey/interview chatbots, all the factors discussed earlier in this article still apply. However, proactive chatbots are more than a simple combination of two types of chatbots, 4 additional factors should be considered when selecting an AI chatbot platform to develop a proactive chatbot.
Interactional intelligence
In addition to language skills powered by generative AI (LLMs), a proactive chatbot must also have interactional intelligence that enables it to concentrate on the task at hand while making users feel heard and delivering a pleasant and effective engagement. It actively engages with users, guiding and nudging them to accomplish complex tasks (e.g., tutoring a user to learn a skill or advising a user to come up with an individualized career development plan). It handles user interruptions gracefully and diligently maintains a conversation agenda to ensure task completion (Image 4.1). Most platforms require chatbot designers to manually track and maintain conversation flow in order to handle disruptions or exceptions, which is impractical given the number of potential interruptions that may occur anytime at any depth of a conversation. Thus, it's crucial that a chatbot platform is equipped with built-in interactional intelligence.

Personal intelligence
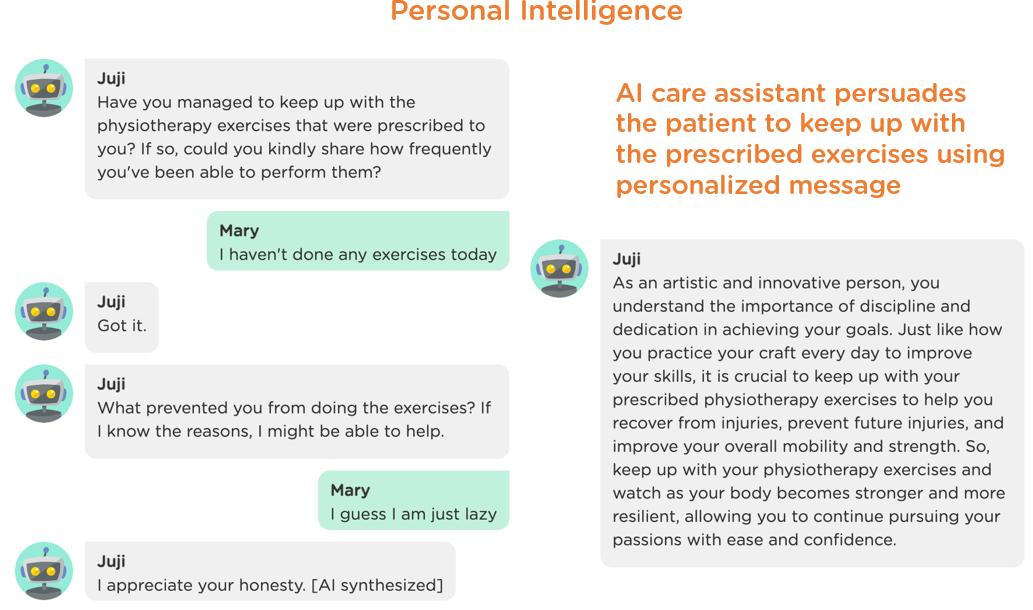
Since a proactive chatbot is meant to automate high-touch services, it is also required to have personal intelligence: the abilities to read between the lines to infer the users' unspoken needs and wants from a conversation, and personalize each interaction accordingly to better guide/persuade the users to make complex decisions or take proper actions. For example, an AI care assistant can infer a patient's motivations and personality and persuade them to adhere to care routines with stories that they can easily relate to and be motivated by (Image 4.2). It is non-trivial to power AI chatbots with personal intelligence, so make sure to ask whether and how your chatbot can acquire personal intelligence when selecting an AI chatbot platform.
Prudence
Since proactive AI chatbots leverage generative AI, unavoidably, they face the same AI safety challenges faced by any other generative AI application. Because of their complex nature and often sensitive use cases (e.g., aiding human essential services in education and healthcare), it is paramount that organizations looking to adopt proactive AI chatbots must have controls and governance tools in place for the safe use of such chatbots. When looking for AI chatbot platforms to build proactive AI chatbots, make sure to ask whether and what kind of AI safety control measures and configurations are in place to ensure safe applications of proactive AI chatbots (Image 4.3).

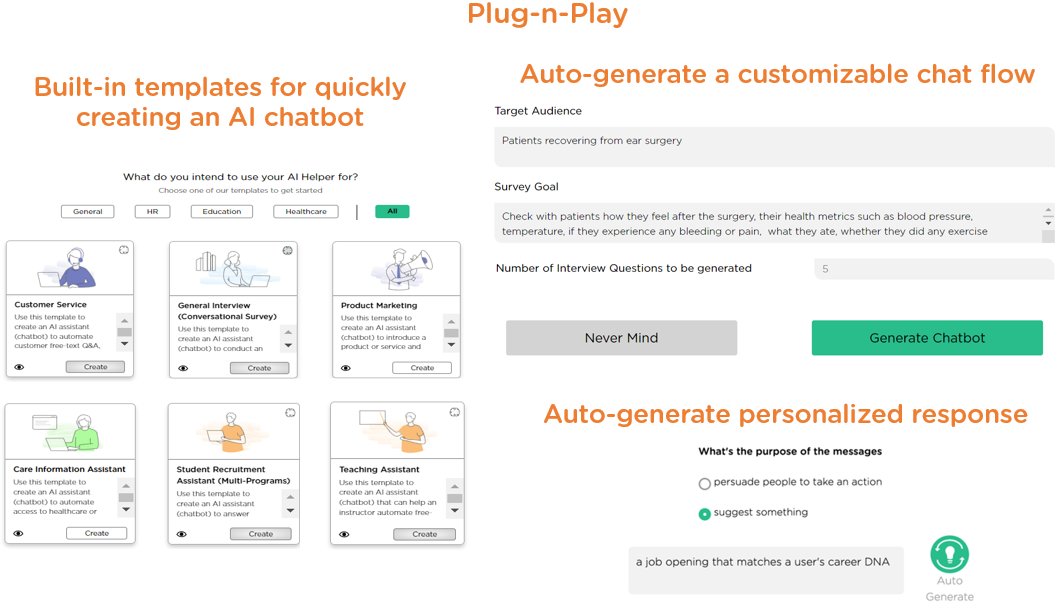
Plug-n-play
Building a proactive AI chatbot with interactional intelligence, personal intelligence, and prudence from scratch may require deep AI + IT expertise and cost millions of dollars and multiple years of efforts. When selecting an AI platform for building proactive AI chatbots, make sure to ask who would need to build, customize, operate, and maintain such a chatbot and typically how long it takes to do so. Built-in AI chatbot templates/assets and fast, no-code customization are always desired (Image 4.4), which in turn significantly impact time-to-value and AI ROI.
Conclusion
By identifying the right type of chatbots for your business needs and considering the relevant key factors outlined in this article, you should be able to select an AI chatbot platform that enables the development of effective chatbots to enhance your service offerings.