What is "conversational"? By the Merriam-Webster dictionary, conversation is defined as an "oral exchange of sentiments, observations, opinions, or ideas". Because of the exchange, one-on-one conversations are often considered the most effective way for humans to engage with one another.
However, human-driven conversations don't scale. From our conversations with universities, we learn that it is not unusual for an admissions office to have only four to five staff members, who might need to handle over 30,000 to 40,0000 incoming student inquiries, not to mention that many such inquiries are repetitive on the similar topic , e.g., program requirements, financial aid options, and application process. Additionally, universities wish to learn more about prospective students who made such inquiries, such as their interest and expectations, which will enable university staff to better follow up with the students (e.g., inviting them to apply for a program or scheduling an interview). So what capabilities must a chatbot have in order to help universities automate such engagements but without losing a human touch?
What is a Conversational Chatbot
To scale out human-driven conversations while containing cost, more and more universities now are enlisting the help of chatbots. Now you might be puzzled: how could a chatbot be not conversational? From the literal sense, it makes absolutely no sense if a chatbot is not conversational. In reality, however most chatbots out there unfortunately cannot converse with their users, hence are not conversational.
How can chatbots be made conversational? To possess human conversation skills, conversational chatbots must be powered by cognitive intelligence—an advanced, human-like Artificial Intelligence (AI). Such a chatbot, also known as a cognitive AI assistant or a cognitive AI chatbot, should demonstrate three key conversation capabilities.
A Conversational Chatbot Supports Two-Way Communication
We’ve all had the experience with a chatbot where we are clicking buttons and being forced to follow a path that leads nowhere. Frustrated, we give up and try to ask a question directly in the chat window. The chatbot, however confused, responds that it does not understand our input. This is a typical one-way exchange, where a chatbot tries to dictate the whole conversation by following a rigid, pre-defined chat flow, which often leaves users frustrated and unhelped.
In another scenario, a chatbot might open up a conversation with a phrase like "How may I help you?" What happens next is also quite familiar: after texting a question, we receive a chatbot response "Sorry I'm not sure I understand, would you mind rephrasing your question?" Left clueless, we don't know how to rephrase the question and are also afraid no matter how we rephrase the question, the chatbot still could not understand. So we give up. This is another typical one-way exchange, where a chabot tries to let users drive the conversation without providing any guidance, which often results in failed conversations because of today's technology limitations.
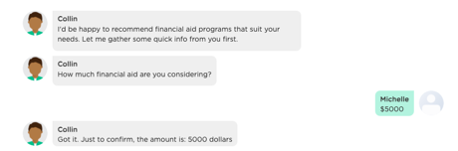
In contrast, conversational chatbots support two-way exchanges, delivering more human-like conversational experiences. Specifically, conversational chatbots can take initiatives and guide a conversation while actively listening to users and allowing users to take initiatives during the conversation. The example below shows a two-way conversation between a chatbot and a student who is inquiring about financial aid options.
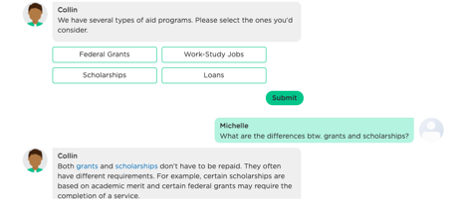
A Conversational Chatbot Understands and Maintains Conversation Context
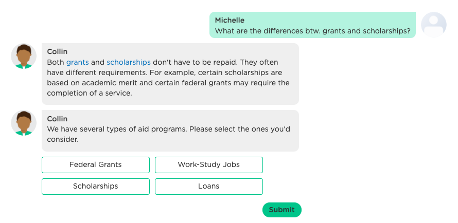
Continuing our above example, a typical chatbot might not recognize and respond to the user's question, even if it did, it would get lost by the user interruption or take us back to the beginning of the conversation. Either way would derail the conversation and fail to complete the intended task (in this case, recommending financial aid programs).
Just like humans in a conversation, conversational chatbots are able to understand the focus of attention and remember the conversation context. As shown below, while a user diverts from the initial flow of the conversation, the chatbot answers the question, and then naturally resumes the flow where it was left off. This conversation capability enables a chatbot to complete assigned tasks while helping users whenever possible.
A Conversational Chatbot Can Read People and Personalize Each Engagement
In addition to language abilities, great human conversationalists have high social-emotional intelligence, which enables them to deeply understand and empathize with their conversation partners and foster effective and pleasant conversations.
Unlike a typical chatbot that often offers one-size-fits-all responses and knows little about its users, a conversational chatbot can actively listen to its users, infer the users' unspoken needs and wants from a conversation, and personalize each conversation. Not only does this capability allow a conversational chatbot to behave more human-like, but also enables it to better help its users based on the users' needs and wants. The conversation example below shows that such a chatbot provides personalized career information to students based on the students' passions, interests, and personality.

Why Adopt a Conversational Chatbot Now?
The demand for personalized, conversational interactions is a growing expectation by today's university students. Multiple university studies show that students are willing to and wish to interact with a chatbot and can also benefit from such interactions. Higher education needs to cut through the clutter and create a better connection with their audience, e.g., current and potential students and alumni. Additionally, university studies indicate that technologies already exist to support rapid, no-coding setup and adoption of cognitive AI assistants, which not only deliver a higher engagement rate, but also continually improve from users' interactions.
In other words, conversational chatbot solutions are no longer a luxury item for only certain universities. Without requiring additional technical resources, EVERY university now can easily adopt cognitive AI technology and their human-like conversational capabilities to improve student/alumni engagements, reduce administrative burdens, and elevate workplace morale, as the university hopes to achieve.