Although powerful large language models (LLMs) like GPT can power a chatbot with abilities to interpret and generate response to user input, they do not really teach the chatbot how to carry out an effective and pleasant dialog with a user. Additionally, AI is far from perfect and there are always cases where AI cannot handle or handles wrong. Hence the role of a conversational AI designer is critical as they put their wisdom and creativity into an AI chatbot and ensure effective dialogs between AI and its users.
In the article “Towards User-Centric Guidelines for Chatbot Conversational Design,” published in the International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, researchers Geovana Ramos Sousa Silva and Edna Dias Canedo at Universidade de Brasília conducted a systematic literature review to uncover best practices in conversational AI design around three areas:
Naturalness
A chatbot should engage in conversations naturally by:
- Presenting itself as a virtual agent with a name and purpose at the start of the conversation.
- Addressing the user by their name when possible.
- Supporting small talk or chitchat, such as greetings and expressions of praise or thanks.
- Echoing user input in responses when appropriate.
- Conveying information in a conversational, casual tone.
- Using alternative ways of saying the same thing, avoiding repetitive messages.
Emotionality
A chatbot should express and understand emotions to build deeper connections with users by:
- Using punctuations, images, GIFs, and emojis to convey emotions and make conversations more engaging.
- Showing empathy by adapting responses based on the user’s feelings.
- Incorporating humor appropriately.
Transparency
A chatbot should be honest and clear about its capabilities to set the right user expectations by:
- Presenting its purpose and capabilities at the start of the conversation.
- Acknowledging its limitations upfront or after a failure.
- Suggesting conversation topics to keep the user on track of what the chatbot can do.
- Asking for clarification when it fails to understand user input.
In the following sections, we will share design tips on how conversational AI designers can apply these best practices when creating AI chatbots.
Best Practice Design Tips to Ensure Naturalness
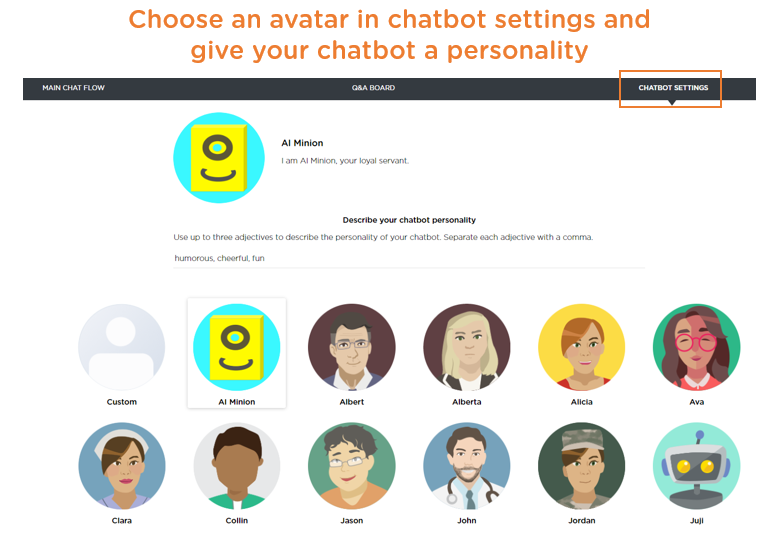
To make AI-human conversations sound natural, a chatbot’s messages should incorporate elements commonly found in human-to-human interactions. Just like meeting any strangers, we often want to have a presence and leave a good first impression. The same applies to an AI chatbot design, giving your chatbot a suitable name along with an avatar (the presence), and even a distinct persona. A chatbot with an avatar (vs. a blank profile) makes users feel the existence or "realness" of the chatbot, helping the AI establish rapport and build trust with users and leading to more engaging interactions.
In Juji Studio, one can select from a variety of built-in avatars or upload their own to give a chatbot an identity. One can further customize the chatbot with a description of its personality (Image 1.1).
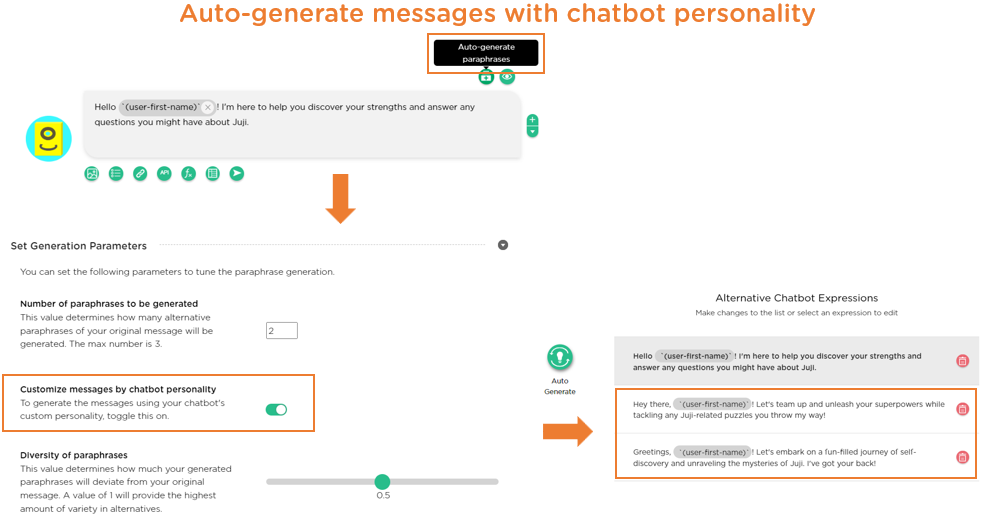
To exhibit the intended personality, a chatbot can use AI to auto-generate its messages based on its personality (Image 1.2). As always, human designers can easily customize or fine-tune AI-generated messages as they see fit.
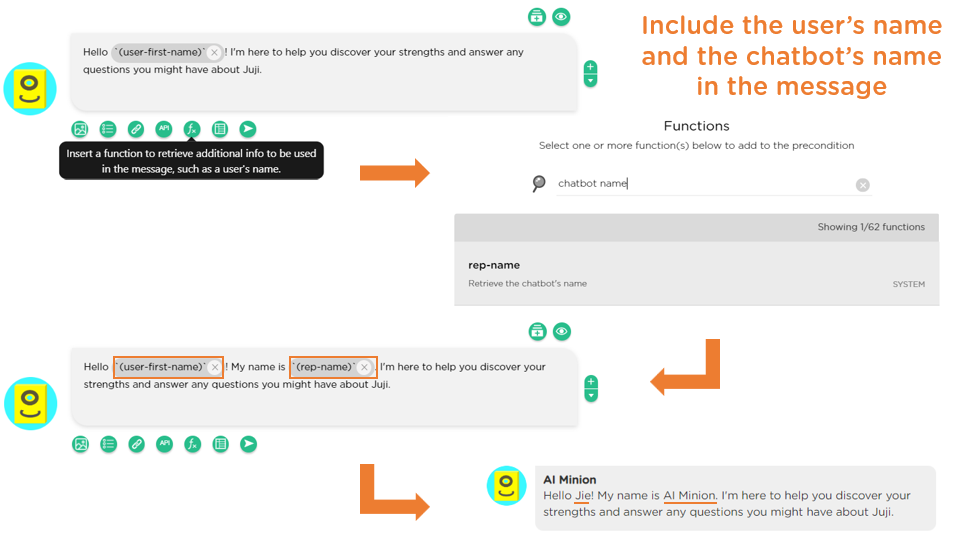
Like in any conversations between strangers, a chatbot should also begin by greeting a user and introducing itself. As part of the introduction, it is always a good idea for the chatbot to explicitly address the user by their name as well as introduce its own name to kick off a conversation naturally (Image 1.3).
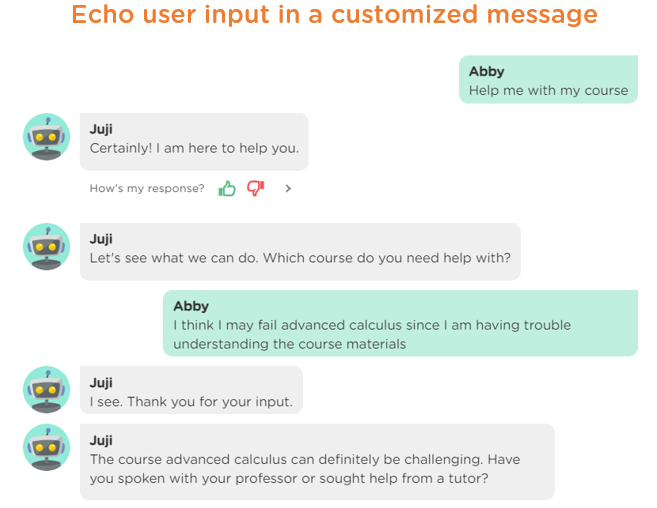
In human conversations, a good listener often echoes or paraphrases what their conversational partner says. This technique not only demonstrates that they are paying attention but also helps to build rapport and ensures mutual understanding. Similarly, in AI-human interactions, a chatbot should employ the same strategy to make the conversation feel more natural and engaging.
Juji Studio enables designers to instruct a chatbot to repeat what it hears in two ways. One way is to extract key information from user input and store it in a custom attribute, which can then be used in a chatbot response to acknowledge the received input or provide context for further conversations. Image 1.4 below demonstrates how to create a custom attribute from user input and use it to tailor a chatbot message.

Image 1.5 showcases this feature in action through an example conversation snippet.
The second way is to simply enable a chatbot to acknowledge what a user says by auto-generating its response, where Juji built-in prompt instructs the chatbot to repeat what it hears (Image 1.6).
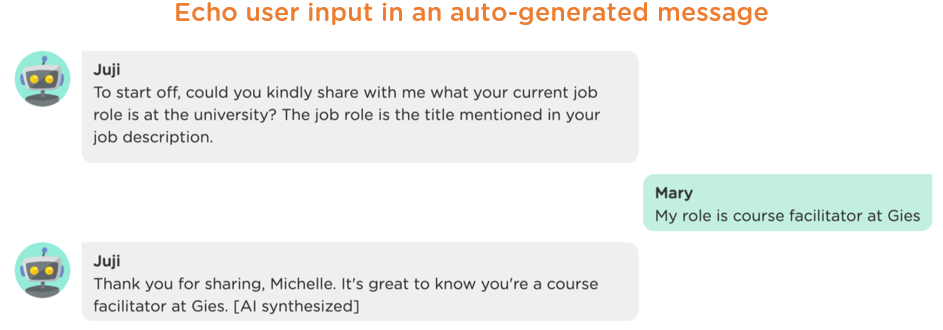
In human conversations, when someone needs to repeat a message or question, they rarely use the exact same wording. Instead, they naturally vary their phrasing to keep the interaction dynamic and engaging, preventing it from sounding monotonous or robotic. Emulating this natural variability is crucial for AI chatbots to create more authentic and human-like interactions.
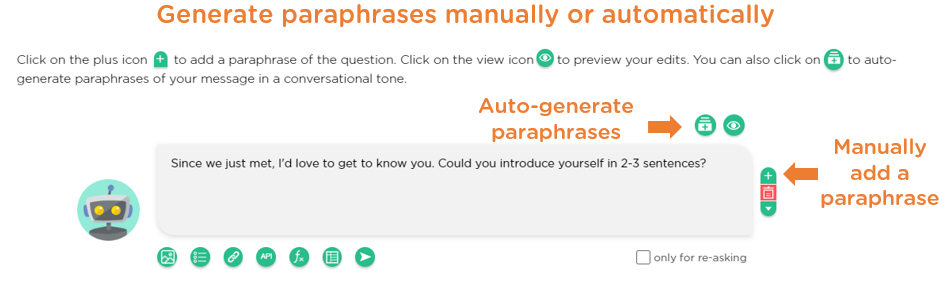
Juji Studio enables designers to define "paraphrases" for any chatbot message or request, either manually or automatically using GenAI (Image 1.7).
A unique feature of Juji Studio is that it allows designers to use the "only for re-asking" checkbox to distinguish between longer paraphrases that provide context and rationale for a question, and shorter, de-contextualized paraphrases suitable for re-asking the question, ensuring the user isn’t confused by repeated information when the question is re-asked (Image 1.8).
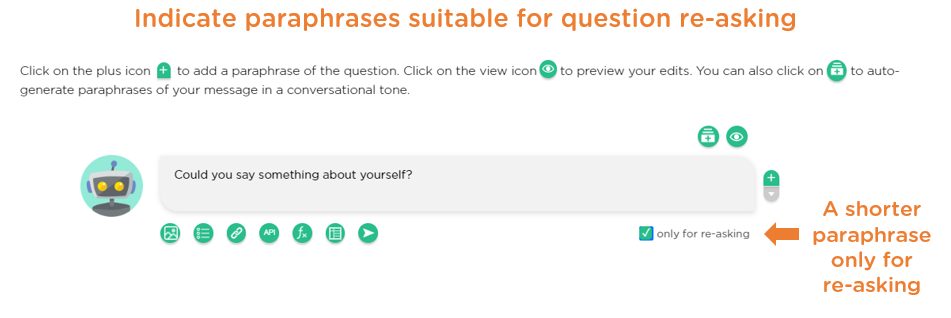
Image 1.9 shows how question paraphrases are used in a chat.

Best Practice Design Tips to Ensure Emotionality
In human-human interactions, emojis convey subtle emotions and add depth to conversations. Similarly, AI can use emojis to express emotional nuances, making interactions feel more personal and relatable. Additionally, AI should interpret emojis in user input to recognize emotional cues and respond accordingly.
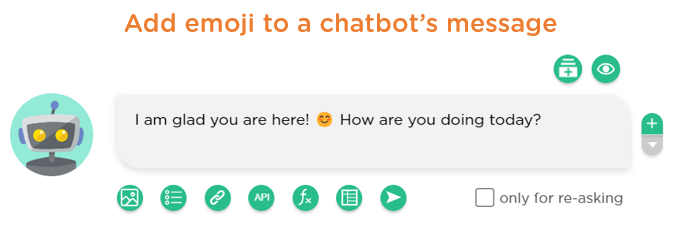
In Juji Studio, designers can add emojis to a chatbot’s message by copying and pasting the corresponding Unicode emoji character, e.g., 😊 (Image 2.1).
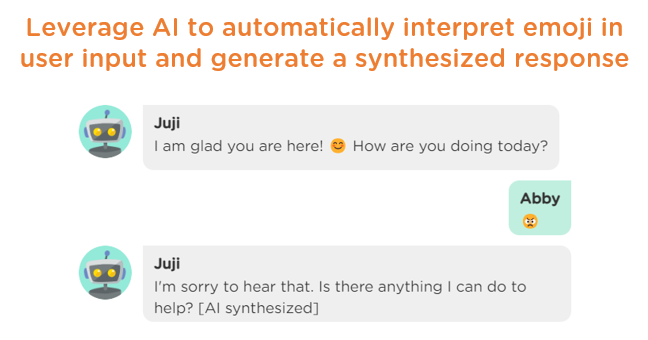
Juji AI can automatically interpret emojis in user input and generate appropriate responses (Image 2.2).
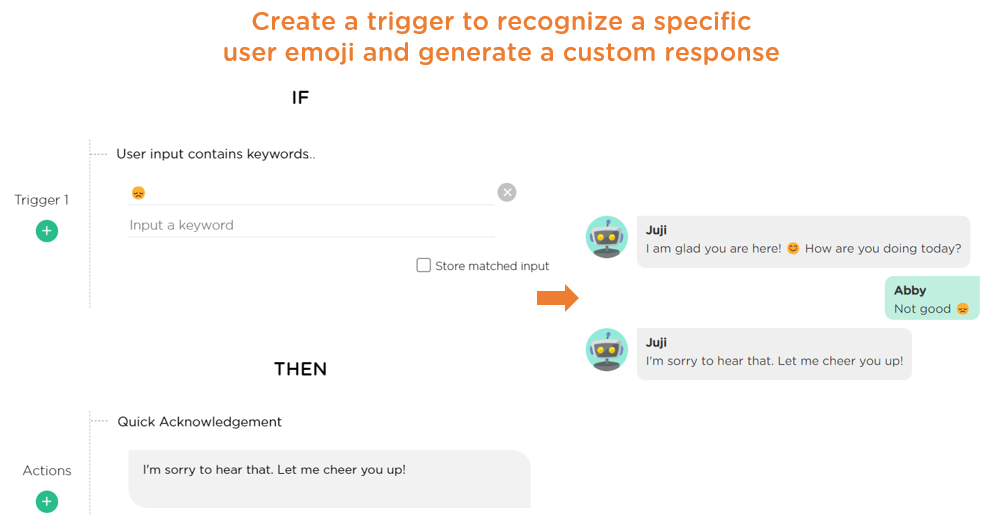
To recognize a specific user emoji and respond with a custom message, create a "trigger" under the “Customize Chatbot Response” section to enable keyword matching with a specific emoji and define a custom response when such an emoji appears (Image 2.3).
Visual elements like images and videos make AI-human conversations more engaging and effective. They provide context, make explanations clearer, and add dynamism to interactions, keeping users engaged and improving their overall experience.
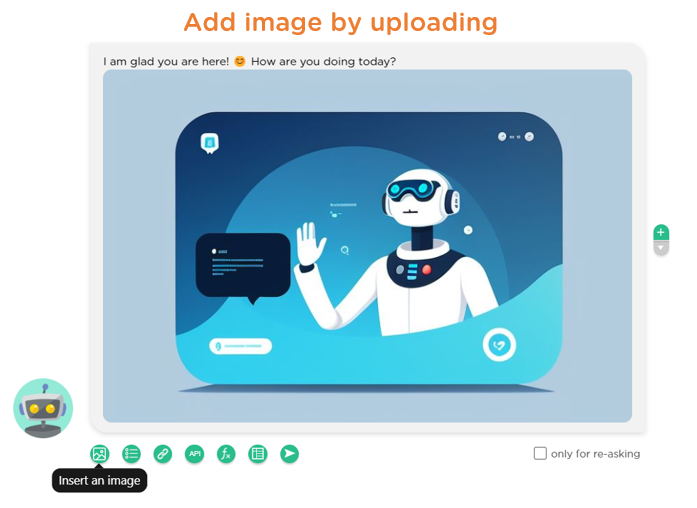
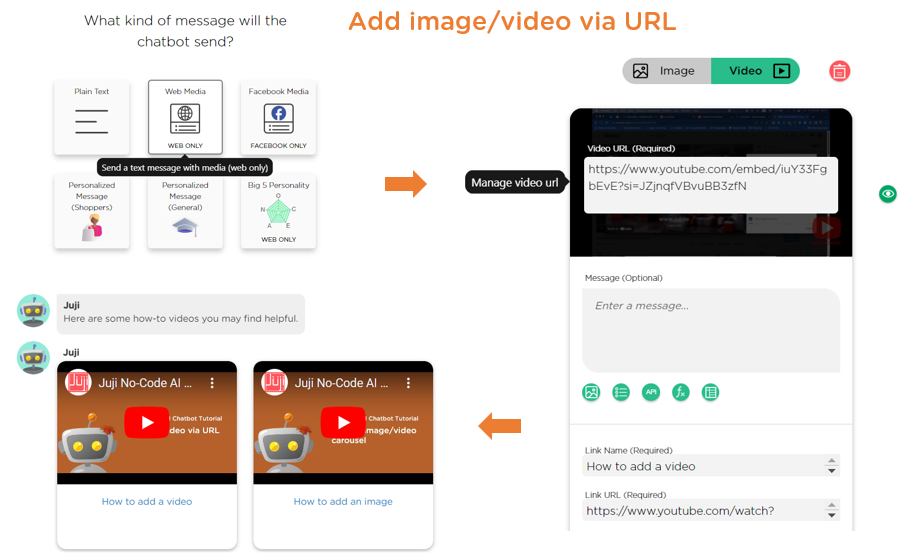
In Juji Studio, designers can incorporate visual elements in two ways: inserting an inline visual element or an independent visual message card. Specifically, designers can insert an image as part of a chatbot message (Image 2.4) or create a “Web Media” card to display images or videos individually or in a carousel (Image 2.5).
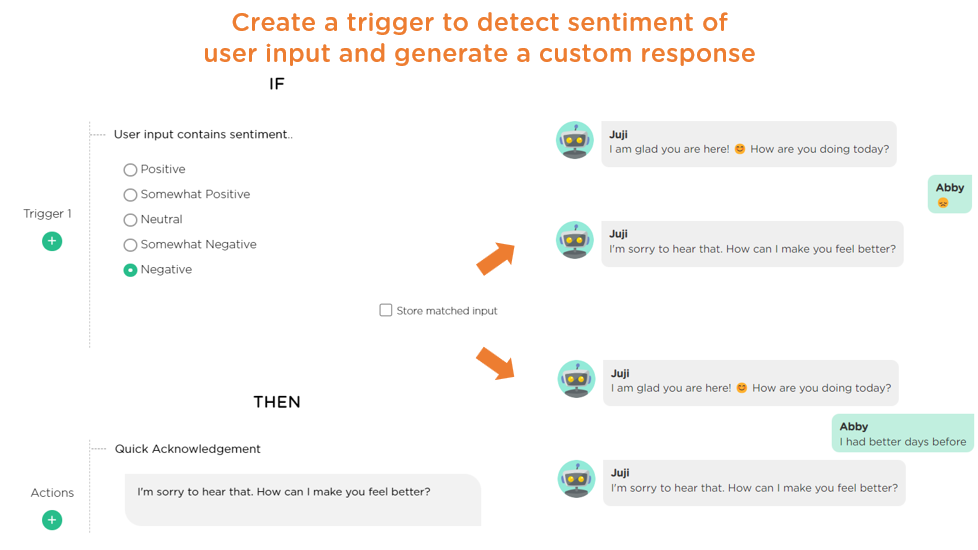
Empathy builds deeper connections in human interactions, making individuals feel understood and valued. Similarly, when AI recognizes and responds to user sentiment empathetically, it creates emotional connections, leading to more productive and positive exchanges.
In Juji Studio, designers can easily configure a chatbot to detect and acknowledge user sentiment in a controlled, custom way (Image 2.6), demonstrating AI empathy.
Best Practice Design Tips to Ensure Transparency
One of the guidelines to ensure transparency is that a chatbot should be upfront about its purpose and capabilities to set clear expectations and build trust with its users.
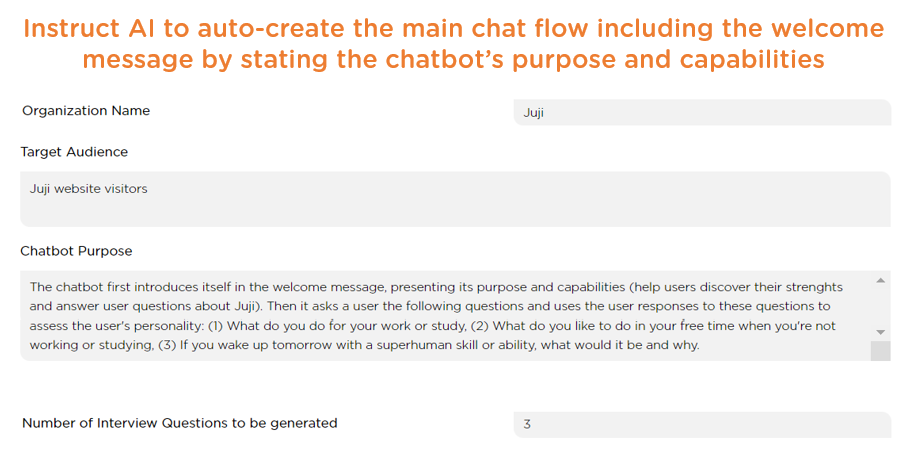
Juji Studio supports designers to do so in two ways. First, when a designer instructs Juji to generate an AI chatbot, they will be asked to explicitly state the following information: the organization that the chatbot is created for, the target audience of the chatbot, and the purpose of the chatbot (Image 3.1).
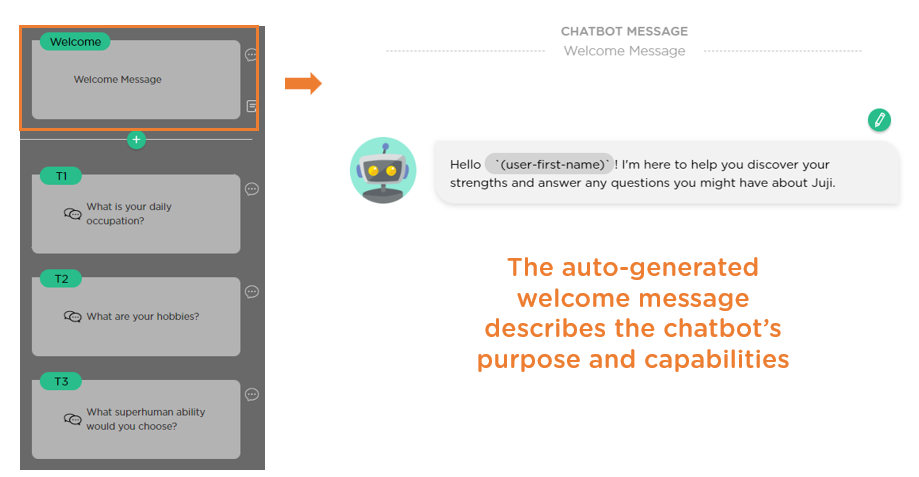
Given this information, Juji automatically generates an AI chatbot including its "Welcome" message (Image 3.2). As displayed in Image 3.2, the generated "Welcome" message, which the chatbot uses to start a conversation with a user, clearly explains the chatbot’s purpose and capabilities, setting the user's expectations.
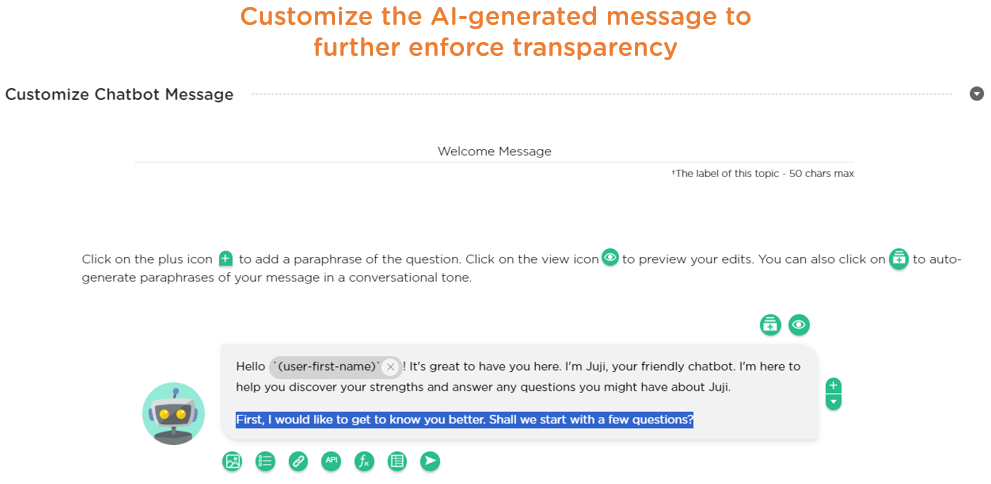
Second, experienced designers can either craft their own welcome messages or customize the AI-generated message (Image 3.3) to further enforce the AI design best practice of being transparent about the AI's purpose and capabilities.
Another guideline to ensure transparency is to keep users informed on what the chatbot can do. This is especially important for proactive chatbots, which are designed to actively guide users to achieve their goals. Here we discuss three scenarios:
- Suggest Starter Topics to Jump Start User-AI Chat
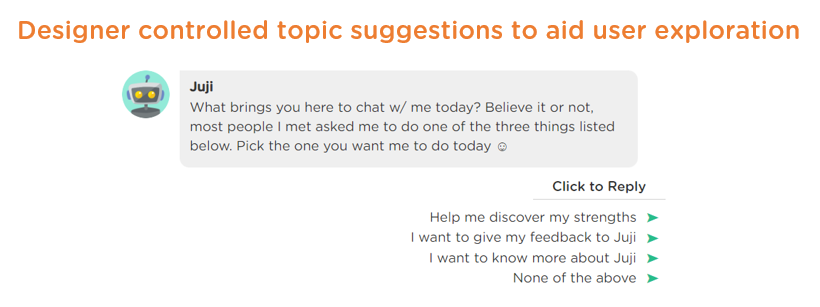
When a user meets with a chatbot for the first time, the user might not know what the chatbot can do. It's a good practice for designers to teach the chatbot to suggest a hand-picked set of initial/popular topics (Image 3.4). Even better, the starter topics can be dynamically selected based on certain criteria, e.g., suggesting the most popular topics or the newest topics that the chatbot just learned (Image 3.5). Just like the road signs on a map, these starter topics enable users to start their exploration.

- Suggest Relevant Topics to Enable Users to Learn More
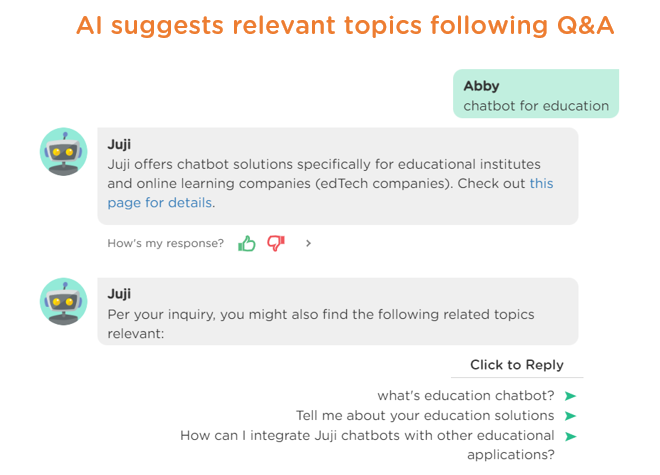
When a user asks a question and a chatbot answers, it is often the case that the user may want to know more about relevant topics. It would be helpful for a proactive AI chatbot to present a few relevant topics after answering the user's question. This enables the user to learn more (Image 3.6). In the case where a user's inquiry is vague and ambiguous, a proactive AI chatbot can suggest relevant topics for the user to clarify their intention (Image 3.7). This approach beats asking a user to rephrase their requests BLINDLY without guidance.

- Suggest Related Topics to Enable Users to Learn More Deeply
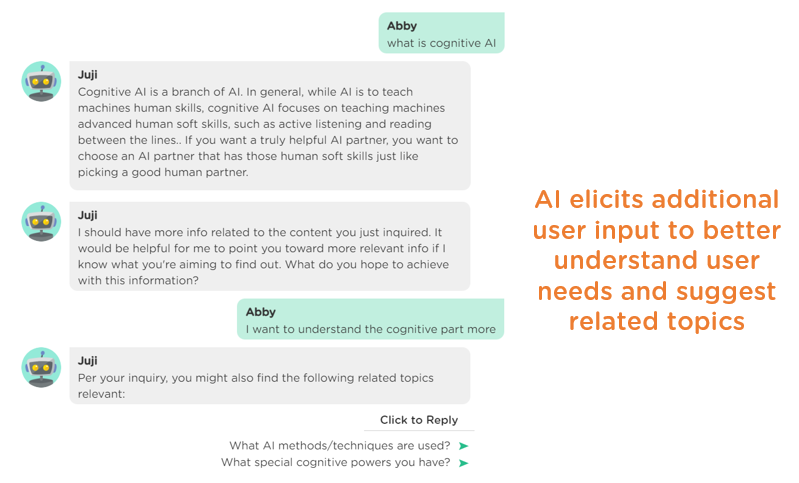
Sometimes, a topic may be complex, involving several sub-topics. In such a case, a proactive AI chatbot could better guide a user to drill down on the specific information more effectively by eliciting additional user input to better understand their needs and then recommend related topics accordingly (Image 3.8).
All the best practices mentioned above are already built into Juji Studio and configurable by designers, who can then instill more transparency into their AI chatbots.
In summary, by ensuring naturalness, emotionality, and transparency in your chatbot design, you can create more engaging user experiences, making AI-human interactions more effective and enjoyable. Juji Studio simplifies the design process even for novice conversational AI designers, fostering user trust and satisfaction from the very start of an AI-human engagement.




