Juji Cognitive AI Chat API¶
The Juji Cognitive AI Chat API enables developers to create an end-to-end cognitive AI chatbot. It is mainly based on GraphQL. We support cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) so you can interact with Juji from any client-side application that supports GraphQL.
GraphQL Basics¶
Once you've logged in to Juji platform, you can access the in-browser GraphiQL IDE to explore Juji API and execute queries.
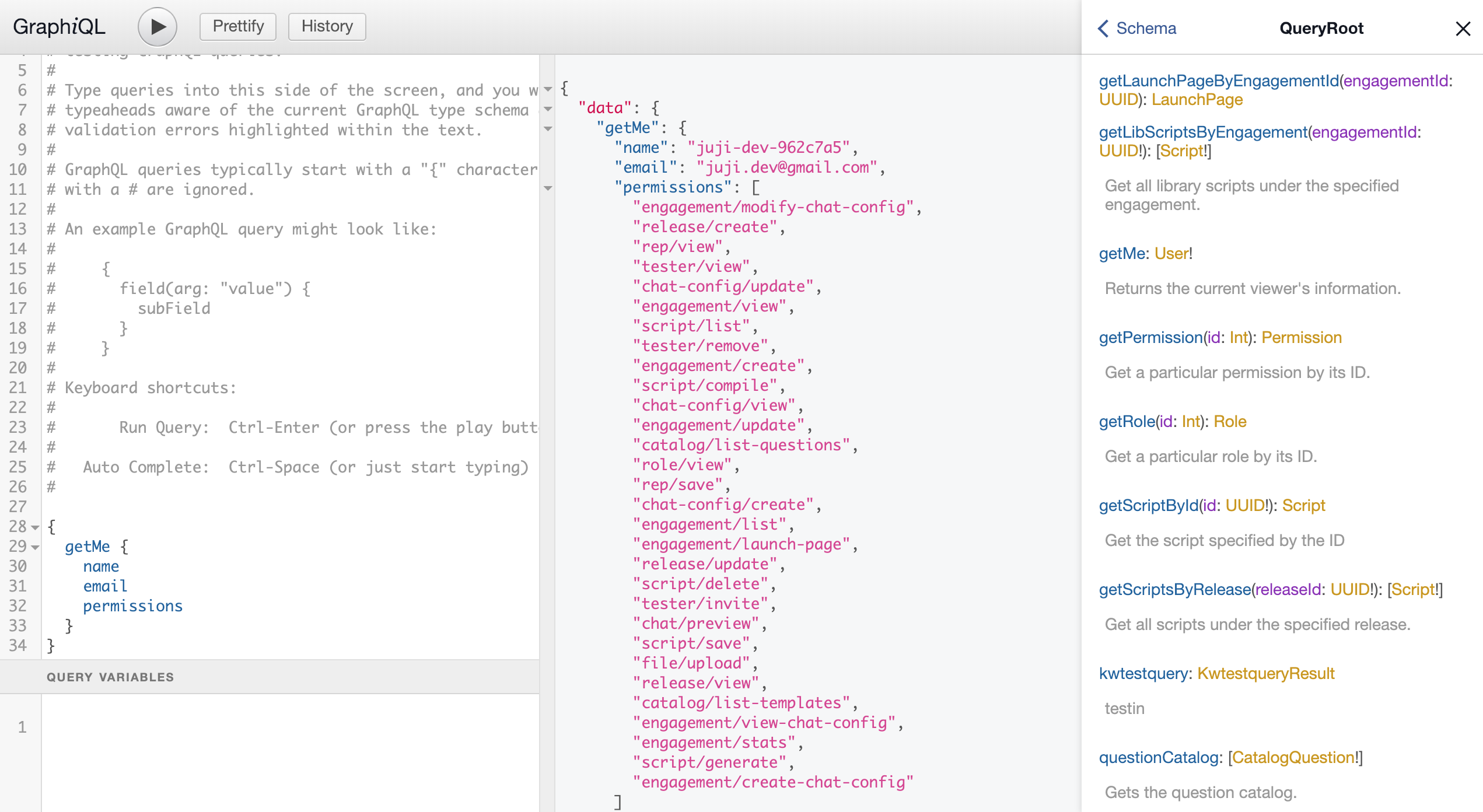
This API reference covers only important concepts of using Juji API. Please use the interactive GraphiQL IDE to read the detailed documentation of all Juji GraphQL API calls.
For your code to access the API, put this GraphQL API endpoint https://juji.ai/api/graphql in your code. Please note: this URL is for your code to access, not a destination for human to visit in browser, you will get {"error": "Unknown server resource."} if you open it with a browser.
Data Access¶
You can access meta data as well as results about your chat engagements over the
GraphQL API at https://juji.ai/api/graphql
An example GraphQL query to list all engagements of a brand:
query
engagements($brandName: String!) {
getEngagementsByBrand(brandName: $brandName) {
name
order
status
}
}
with the variable brandName specified in an JSON object:
{
brandName: "mycorp"
}
Consult the documentation of your GraphQL client library on the details of submitting GraphQL queries.
Output Format¶
Our API can return data in JSON, EDN as well as Transit format.
You can specify how you want to receive API responses by including the Accept header set to any one of:
application/json(default)application/ednapplication/transit+json
The advantages of EDN and Transit are richer data types. With Transit you also get a more efficient over the wire format.
Errors¶
GraphQL always returns a 200 HTTP response status code, so we have to rely on
the errors field of the response to check for errors.
Per the GraphQL specification, errors is an array of maps (dictionaries). Each error map will have the following keys message, category, kind and data. data is any valid JSON or EDN value and the other fields are all strings. There are five (5) broad categories of errors authentication, authorization, validation, application and unexpected. Within each category, kind explicitly identifies the actual error.
For example, an authentication errors look like:
{
"category": "authentication",
"kind": "auth.error/not-authenticated",
"message": "The operation requires you to be authenticated.",
"data": {}
}
Websocket¶
Some computational intensive API requests are handled with Websocket, so the results
can stream in when they become available. Since WebSocket requests cannot set custom headers, the JWT token should be sent as a query parameter auth-token.
Programmatic Chatbots Creation and Deployment¶
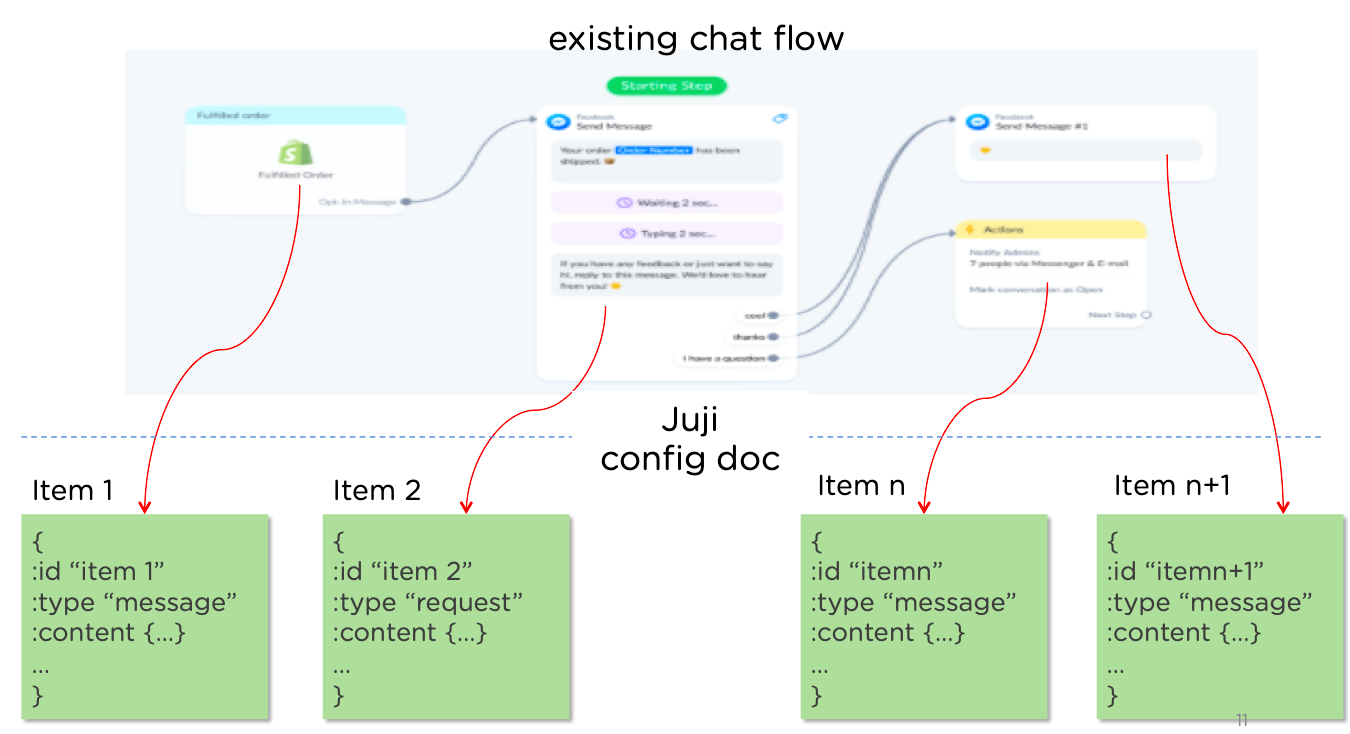
This guide is for users who enjoy Juji chatbot's powerful dialog management, but prefer using their own interfaces to create chatflow. For example, one can take an existing chat flow created in another platform, convert it to Juji's chatflow format. Then use Juji APIs to create and deploy the chatbot on Juji. In other words, it is possible to programmatically create and deploy chatbots on the Juji platform. You just need to follow three simple steps:
Create a Juji Account and Login¶
A valid Juji account is necessary for using most of the APIs. It is also the only step you have to complete using the Juji website. Simply go to Juji Signup page to create an account if you haven't yet done so.
Once you have an account, you can use the authenticate GraphQL mutation to log into your account and start a session.
mutation Authenticate($input: AuthenticateInput!){
authenticate(input: $input) {
token
}
}
You may also need your account's brand id, you can use the following GraphQL query to access it.
query GetBrands{
getBrands{
name
}
}
Create a Chatbot and Customize It¶
A chatbot lives in an engagement. In order to customize a chatbot, you either creates an engagement or uses an existing engagement.
// To create engagement with default blank template
mutation CreateEngagement($input: CreateEngagementInput!){
createEngagement(input: $input) {
engagement{
name
id
order
status
}
}
}
// To list existing engagements
query Engagements($brandName: String!) {
getEngagementsByBrand(brandName: $brandName) {
name
id
order
status
}
}
Then you can 1) update your chatflow by uploading a customized config-doc and/or 2) update your Q&As by uploading a customized Q&A csv file.
// Set isJson to true if the the config-doc is in JSON format,
// otherwise, Clojure EDN format is expected.
mutation UpdateChatConfig($input: UpdateChatConfigInput!){
updateChatConfig(input: $input) {
message
success
}
}
To update your Q&As, you will need to send a POST request. Below is a cURL snippet generated from Postman.
# overwrite is optional, remove it if you want to add the Q&As onto existing ones
curl --location --request POST 'https://juji.ai/api/faq-upload/<brand-id>/<engagement-order>' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <token>' \
--form 'overwrite=1' \
--form 'file-content=ID,Question,Answer,Comment,Multi-turn Q&A,# of asking
help,Help,Here comes help!,,,
help,Can you help me?,,,,'
Launch Your Chatbot¶
Once the chatbot is ready, you can deploy it by creating a web release.
mutation CreateRelease($input: CreateReleaseInput!){
createRelease(input: $input) {
id
order
type
}
}
The web release can be accessed at https://juji.ai/pre-chat/<engagement-id> using a browser or API calls. Please refer to the chat section below for details on how to use API calls to chat.
You can continue to improve your chatbot after you have made a release - simply update your config-doc and/or Q&As and then make a new release. The pre-chat URL above will always point to the latest web release.
Chat¶
It is easy to write a chat client that talks with a Juji chatbot via Juji Chat API. For example, it takes less than 200 line of Javascript code to write a client that chats with a Juji bot, see
Juji's chat experience is built on top of WebSocket to push data to the client. This requires using GraphQL subscription to enable the server to push data to your client. Invoking a GraphQL subscription must be done over WebSocket because data will be streamed in and the connection must be kept open.
Clients can be written in any programming language that supports Websocket. For example, most Web browsers support this Javascript Websocket API, so it is easy to write a Juji client that works for Web browsers.
Note that you don't need authentication to create a participation and start chatting. You just need a deployed chatbot.
The following steps are required to initiate a chat session via the API:
Create participation¶
First, note the Web release URL of the REP, e.g.
https://juji.ai/pre-chat/5f4d4a16-9471-4b84-a26a-94a286a38c63. Make a HTTP POST request to that URL
with the following form data:
| Field Name | Required? |
|---|---|
firstName |
Yes |
lastName |
No |
email |
No |
Only first name is required, so that the bot can address the user. Data in JSON format is also supported.
For example, using the Fetch API of a Web browser, you may create a request like this:
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append('firstName', 'John');
const request = new Request('https://juji.ai/pre-chat/5f4d4a16-9471-4b84-a26a-94a286a38c63',
{method: 'POST', body: formData});
fetch(request)
.then(response => {
if (response.status === 200) {
return response.json();
} else {
throw new Error('Something went wrong on api server!');
}
})
.then(response => {
console.debug(response);
// ...
}).catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
A successful POST request returns a JSON object looks like this:
{
"chatUrl": "https://juji.ai/chat/5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0",
"participationId": "5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0",
"websocketUrl": "wss://juji.ai/api/v1/ws"
}
The returned JSON object contains two pieces of information needed to initiate a WebSocket connection to start the chat: participationId and websocketUrl. In addition, it also contains the chatUrl which can be used to enter the prebuilt Juji chat page.
Failed POST request returns a JSON object with an error field with an error message string.
Establish WebSocket connection¶
A WebSocket connection with the server can now be established by doing a HTTP GET
on the returned websocketUrl value above.
A successful GET request will upgrade the connection to the WebSocket protocol, or an
error message will be returned.
In the case of a Web browser, the constructor of the Websocket Javascript object will do this for you. For example:
const socket = new WebSocket('wss://juji.ai/api/v1/ws');
Receive chat messages via GraphQL subscription¶
A listener should be registered to watch the status of the Websocket connection,
e.g. using browser JavaScript's WebSocket.onopen event listener. When the connection
is open, the listener should send a chat subscription GraphQL query to the server
over the WebSocket connection. The subscription query looks like this:
subscription {
chat(input: {
participationId: "5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0"
}) {
type
role
text
}
}
soecket.send function:
socket.addEventListener('open', function (event) {
socket.send('subscription {
chat(input: {
participationId: "5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0"
}) {
role
text
type
}
}');
});
role, text and type, but there are other message fields that you could subscribe to as well (see below).
A successful subscription will result in the server sending two messages announcing that the user and the REP have joined the chat:
{
"data": {
"chat": {
"type": "user-joined",
"role": "user",
"text": null
}
}
}
{
"data": {
"chat": {
"type": "user-joined",
"role": "rep",
"text": null
}
}
}
Followed by REP's chat messages if this REP is configued to speak first, e.g.
{
"data": {
"chat": {
"type": "normal",
"role": "rep",
"text": "Hello, John! I am Juji, your virtual interviewer."
}
}
}
To handle these incoming messages in your code, you need to register a listener. For example, to continue our Web browser example:
socket.addEventListener('message', function (event) {
console.log('Message from server ', event.data);
});
type is a required field of Juji chat message. Currently, chat message could be one of the following types:
| Type | Sender | Description |
|---|---|---|
user-joined |
server | REP or user have joined the chat, the start of a participation |
normal |
both | Normal chat messages |
user-left |
server | REP ends the participation |
typing |
client | User is typing |
keep-alive |
both | Server sends during idle to keep connection alive, client can send too |
connection-closed |
server | Server detected that the WebSocket connection to client is lost |
debug |
server | Debug information from the server |
For all the possible fields of the chat subscription, please consult GraphiQL, and look under "subscriptionRoot" - "chat" - "ChatMessage".
For example, if you want the REP to ask choice questions in your chat, you need to add the fields "display" (for displying the choice question) and "move" (for sending user moves that respond to the choice questions) in the subscription.
subscription {
chat(input: {
participationId: "5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0"
}) {
type
role
text
display {
type
data {
type
gid
questions {
kind
wording
heading
qid
choices {
text
value
other
}
}
}
}
move {
value
text
question
gid
}
}
}
Send chat messages¶
The client should send the chat messages over WebSocket connection. The message
is encoded in a saveChatMessage GraphQL mutation, which looks like this:
mutation {
saveChatMessage(input: {
type: "normal"
pid: "5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0"
text: "Hello, nice to meet you."
}) {
success
}
}
pid field should has the same value as the participationId received.
To continue our Web browser example, you would put the above as the argument for soecket.send function:
soecket.send('
mutation {
saveChatMessage(input: {
type: "normal"
pid: "5c3bcc2a-9ce5-40a7-b1da-80c065e283b0"
text: "Hello, nice to meet you."
}) {
success
}
}
');
If successful, the client will receive a status message:
{
"data": {
"saveChatMessage": {
"success": true
}
}
}
If you are sending response to a choice question, the input should include a "move" field.
Download Chat Report¶
Basic Conversation Report¶
Basic chat report can be fetch using GET request.
curl --location --request GET \
'https://juji.ai/api/reports?report-key=individual-results&auth-token=<token-value>&engagement-id=<engagement-id>&include-test-data=false'
https://juji.ai/api/reports and in the query string, set the report-key to "individual-results", then fill in the engagement-id and other optional parameters. Engagement id can be queried using API call such as Engagements or you can find the id as the last part of the generated web URL after you deployed your chatbot. When using API key, auth-token parameter is not required. include-test-data is set to false by default.
The response will be a string of data in csv format. The data includes conversation responses of each participatants of the given engagement. An exameple is shown below.
First Name,Last Name,Email,User Agent,Completion Code,Location,Start,Finish,Duration (minutes),Channel,Gather demographics: gender,Asked FAQs
t1,,juji-user-548327dc-aa1f-4054-8ab4-a37e203e0c26@juji-inc.com,"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_0_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.88 Safari/537.36",,"{:timezone ""America/Los_Angeles"", :ip ""12.34.56.789"", :area-code 0, :dma-code 0, :city ""A"", :country-code ""US"", :metro-code 0, :longitude -123.4567, :postal-code ""12345"", :region ""California"", :org ""AT&T Services, Inc."", :latitude 123.4567, :country-name ""United States""}",2021-01-20 23:24:06,,1,web,,
Optionally you can also include tarit percentile scores in your individual results if you have access to personality analytics. The following boolean parameters can be used to specify the traits you desire:
big5_factorsbig5_facetsholland_codesshopper_dnasoft_skillsmoral_characters
Below is an example using cRUL and well as its response.
curl --location --request GET \
'https://juji.ai/api/reports?report-key=individual-results&auth-token=<token-value>&engagement-id=<engagement-id>&include-test-data=false&big5_factors=True&soft_skills=True'
First Name,Last Name,Email,User Agent,Completion Code,Location,Start (America/Los_Angeles),Finish,Duration (minutes),Channel,Tell me about yourself,Asked FAQs,big5_factors_neuroticism,big5_factors_extroversion,big5_factors_openness,big5_factors_agreeableness,big5_factors_conscientiousness,soft_skills_leadership,soft_skills_people_skills,soft_skills_innovativeness,soft_skills_grit,soft_skills_action_oriented,soft_skills_resourcefulness,soft_skills_inquisitiveness,soft_skills_teamwork,soft_skills_communication,soft_skills_positivity,soft_skills_calmness,soft_skills_independence,soft_skills_detail_oriented,soft_skills_adaptability
John,,juji-user-a3f2ac4e-b614-4151-8b01-839c654109a3@juji-inc.com,"Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/101.0.4951.54 Safari/537.36",,"{:timezone ""America/Los_Angeles"", :ip ""12.34.56.789"", :area-code 0, :dma-code 0, :city ""A"", :country-code ""US"", :metro-code 0, :longitude -123.4567, :postal-code ""12345"", :region ""California"", :org ""AT&T Services, Inc."", :latitude 123.4567, :country-name ""United States""}",2022-05-10 23:14:03,2022-05-10 23:14:33,0,web,I am an AI software engineer at Juji. I train chatbots,,17.066186189512738,9.182373692137357,92.17822650548699,18.897750348327946,92.82761574531013,89.66562210622642,0.44348765009564195,99.34258717762158,93.0057170659342,75.51779746902791,99.95202433931146,99.77415041423164,3.503366467149105,42.572588437085365,18.1462436235978,95.45517236734389,99.99089855797502,93.71164811901794,83.54958737675481
support at(@) juji.io..
Standard Big5 Report¶
Alternatively, there is an API for retrieving Big5 personality scores with trait names. This can be done with the same GET request as the regular individual results API except the report-key is set to big5.
curl --location --request GET \
'https://juji.ai/api/reports?report-key=big5&auth-token=<token-value>&engagement-id=<engagement-id>&include-test-data=false'
Similarly, the response will be a string of data in csv format. The data includes conversation responses and personality scores (if applicable) of each participatants of the given engagement. An exameple is shown below.
First Name,Last Name,Email,User Agent,Completion Code,Location,Start,Finish,Duration (minutes),Channel,Gather demographics: gender,Asked FAQs,Openness,Imagination,Artistic_Interest,Feelings,Adventurousness,Intellectual_Curiosity,Liberalism,Conscientiousness,Self_Efficacy,Orderliness,Dutifulness,Achievement_Striving,Self_Discipline,Cautiousness,Extroversion,Friendliness,Gregariousness,Assertiveness,Activity_Level,Excitement_Seeking,Cheerfulness,Agreeableness,Trust,Straightforwardness,Altruism,Cooperation,Modesty,Sympathy,Neuroticism,Anxiety,Anger,Depression,Self_Consciousness,Impulsiveness,Vulnerability
t1,,juji-user-548327dc-aa1f-4054-8ab4-a37e203e0c26@juji-inc.com,"Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 11_0_1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.88 Safari/537.36",,"{:timezone ""America/Los_Angeles"", :ip ""12.34.56.789"", :area-code 0, :dma-code 0, :city ""A"", :country-code ""US"", :metro-code 0, :longitude -123.4567, :postal-code ""12345"", :region ""California"", :org ""AT&T Services, Inc."", :latitude 123.4567, :country-name ""United States""}",2021-01-20 23:24:06,,1,web,,,36.13541798365461,13.290581805094925,69.90396487992511,77.15953217560208,14.352478113721617,21.452611092889672,20.653339834694272,44.28527848667517,54.561037503275145,82.38387886673544,91.3233545692471,10.616104982056406,19.55675956043462,7.270535438302267,75.0045233539362,84.47620138247996,80.35717998131344,66.9274661801379,54.78618912035408,82.03414681082974,81.44595664850205,82.06446262912935,90.87886328546921,85.49197212672262,83.83877023080315,75.70710344618357,88.70960654682591,67.76046013877169,78.67947741962988,67.04116468437702,86.20177231934017,78.76662084022674,69.74154161142214,99.68790702532878,70.6378580370844
References¶
- Please read about Juji API introduction first for important API concepts to help you better understand this guide. Additional API documentation also includes Juji Cognitive Core API.
- Juji's GraphiQL can be used to explore existing GraphQL APIs and their parameters.
- Juji client github page contains concrete examples written in JavaScript for all the API calls in this guide, please refer to it for detail.